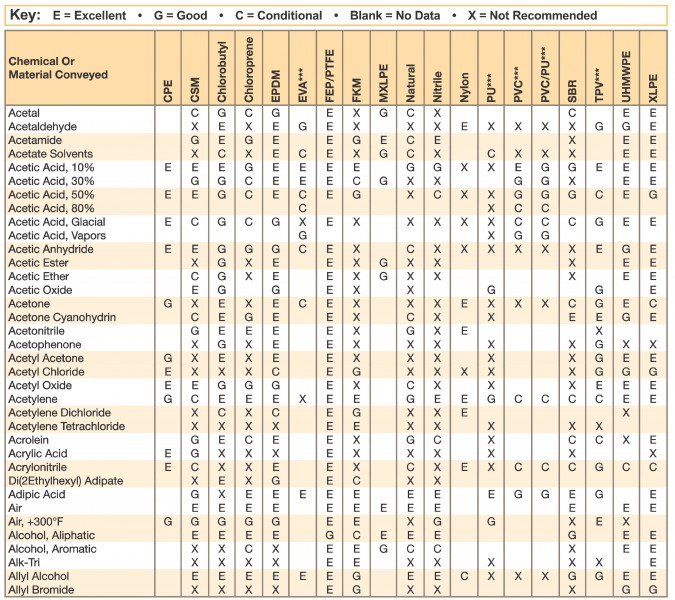
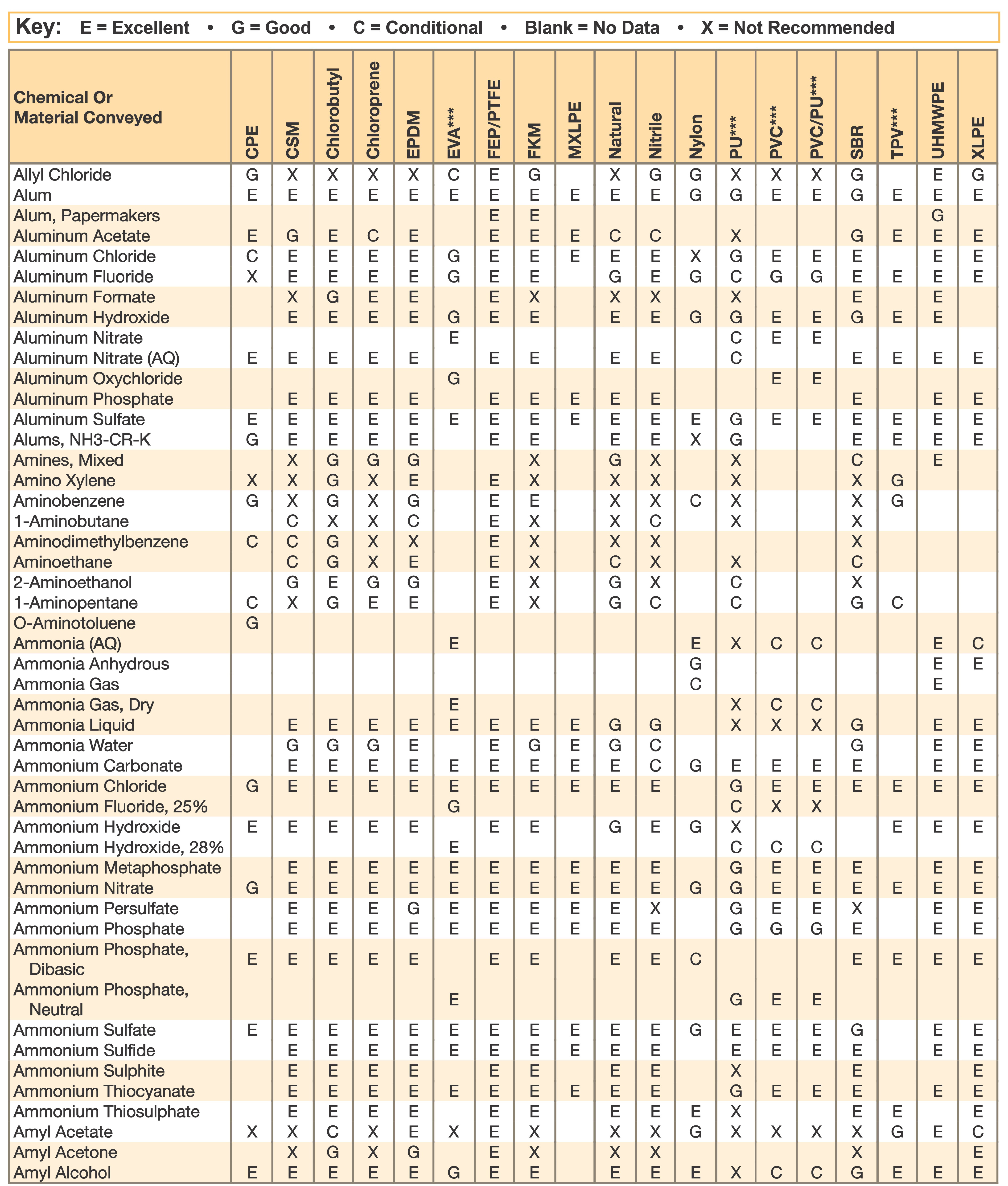
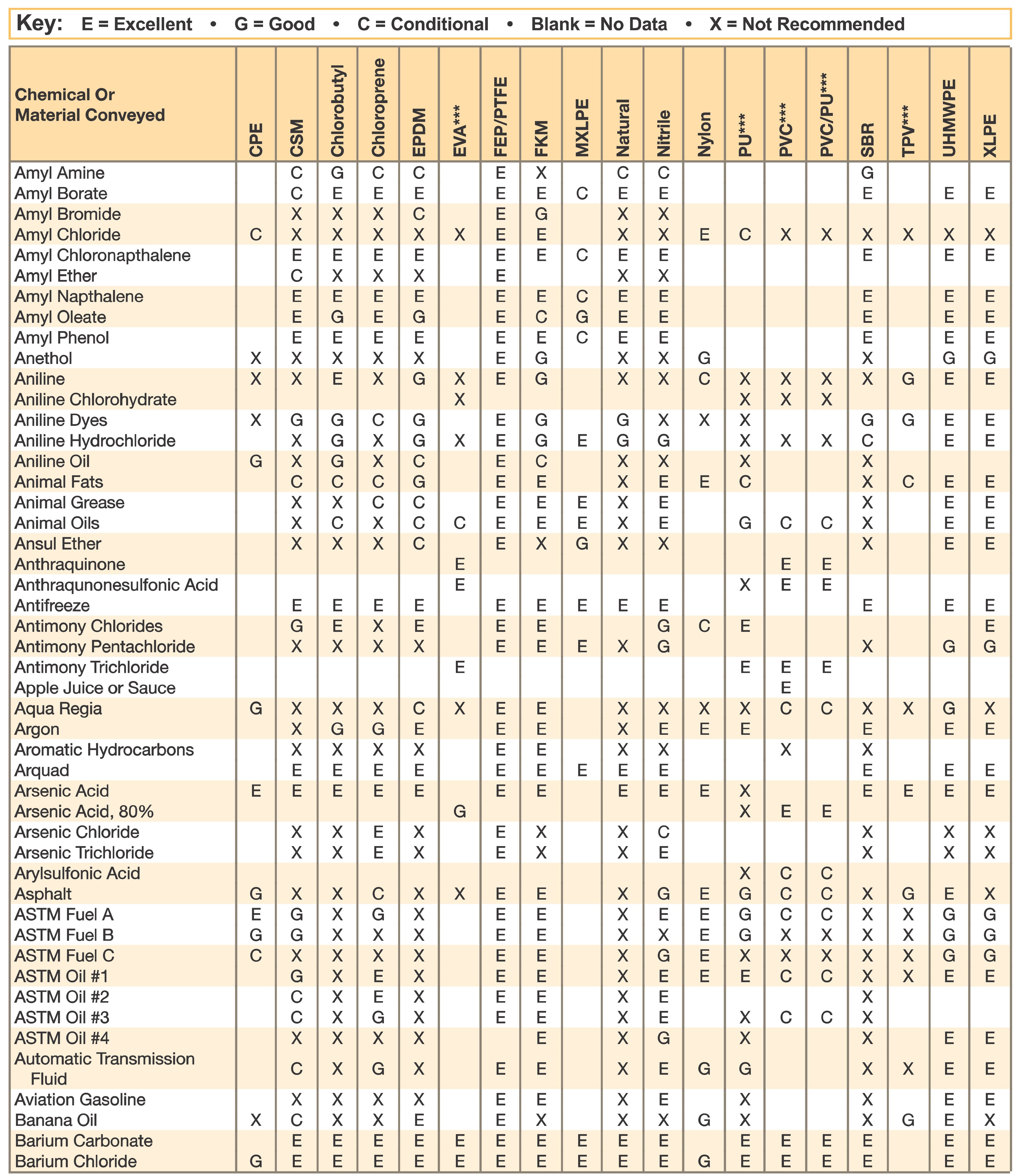
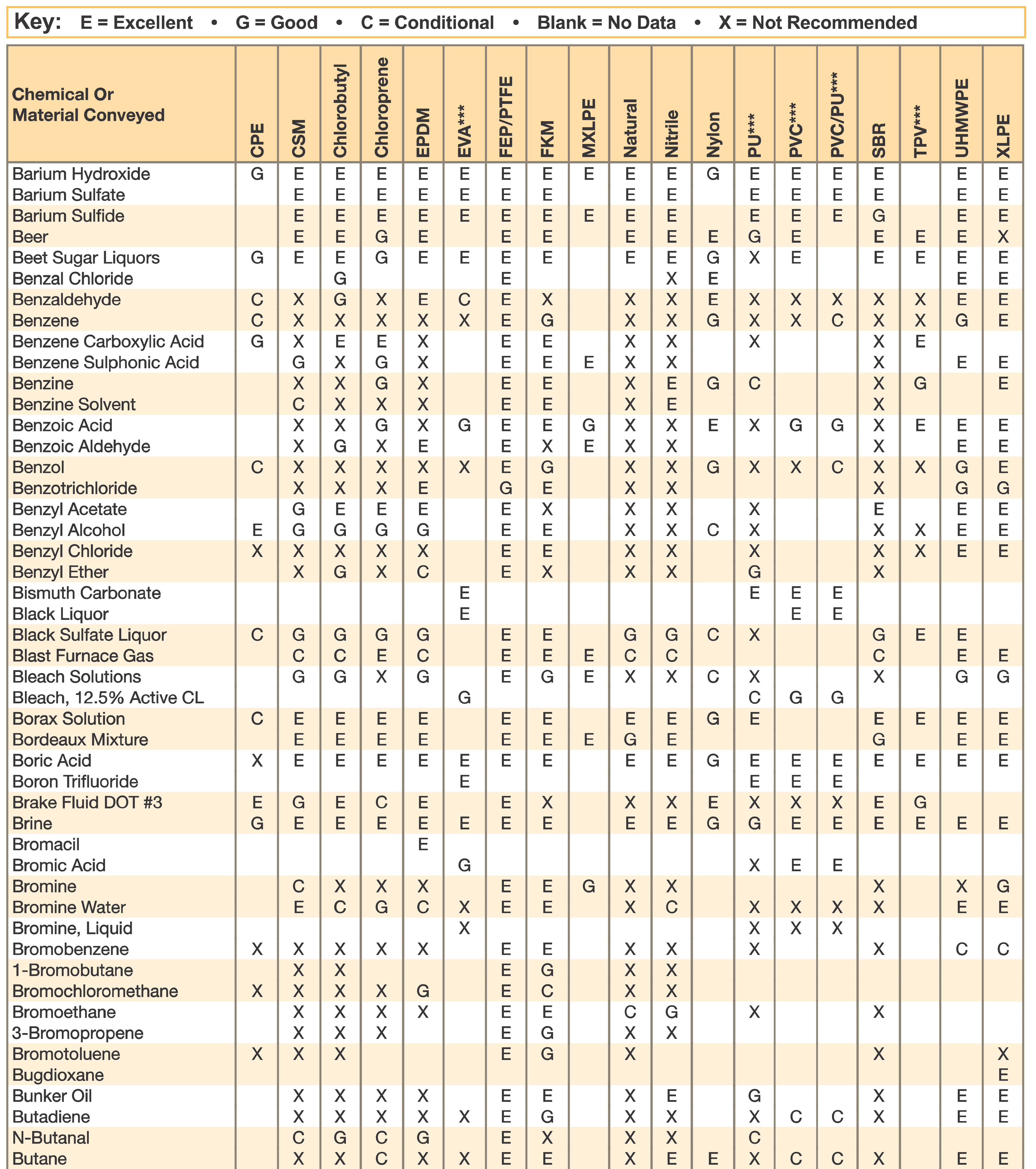
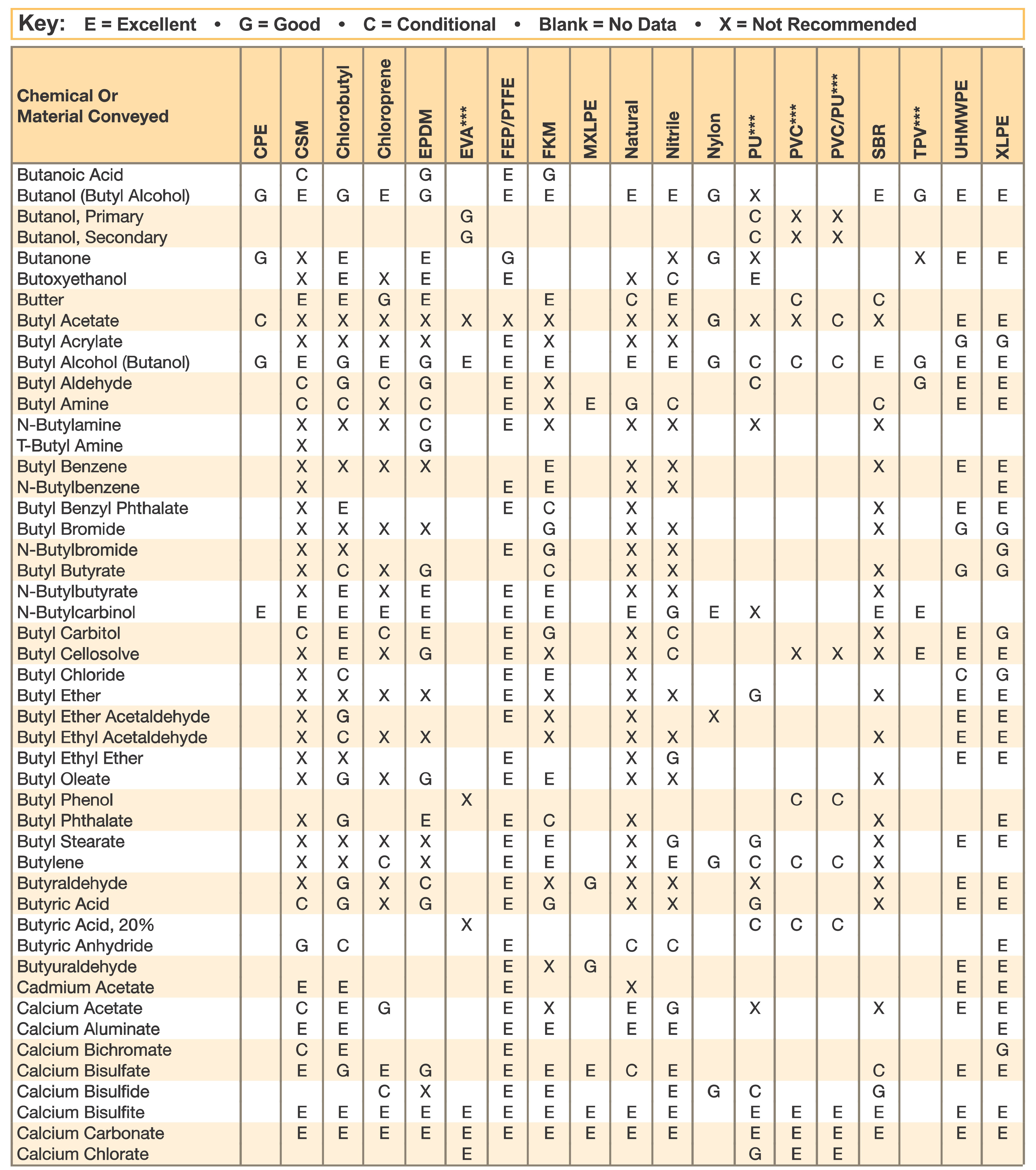
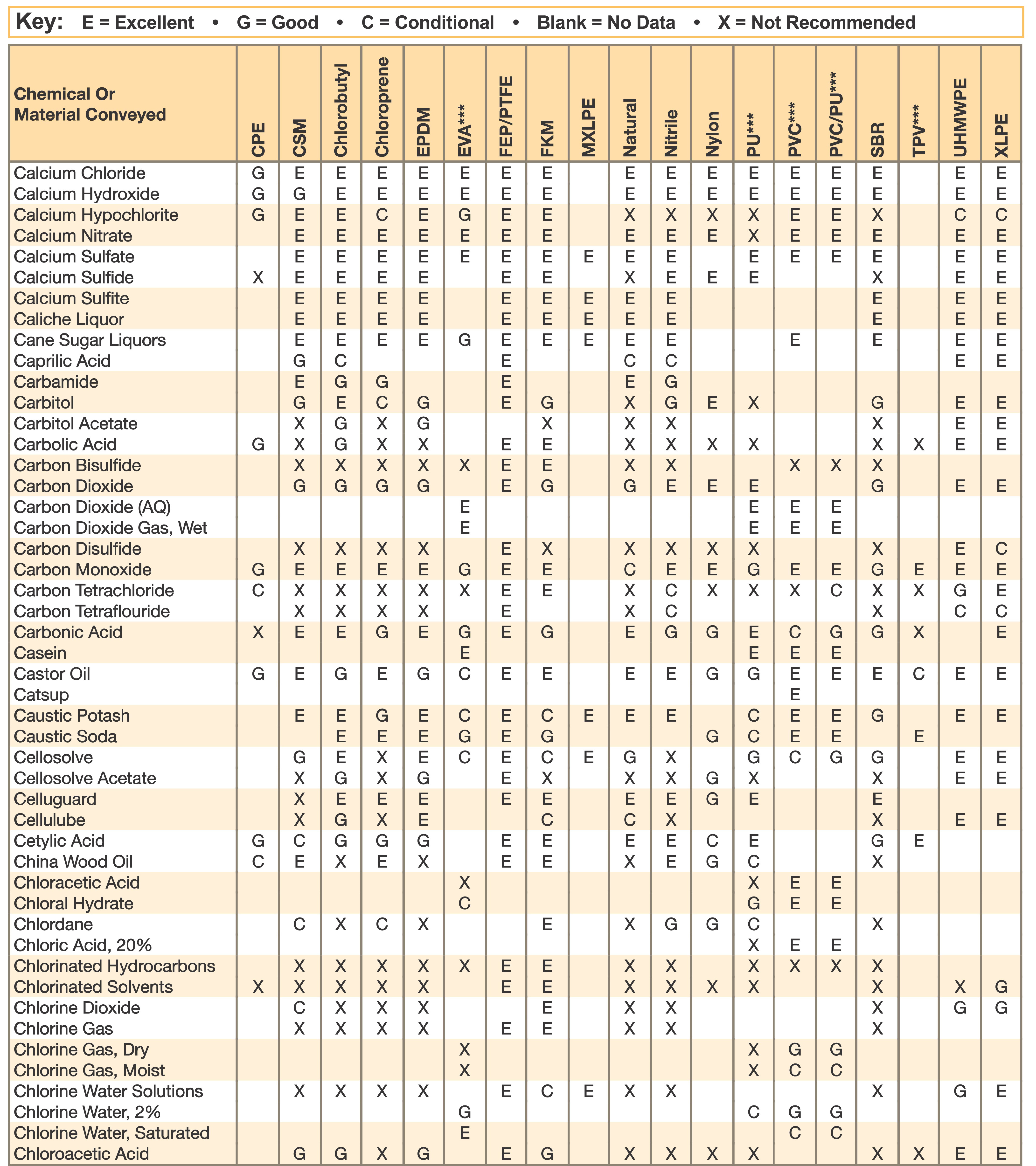
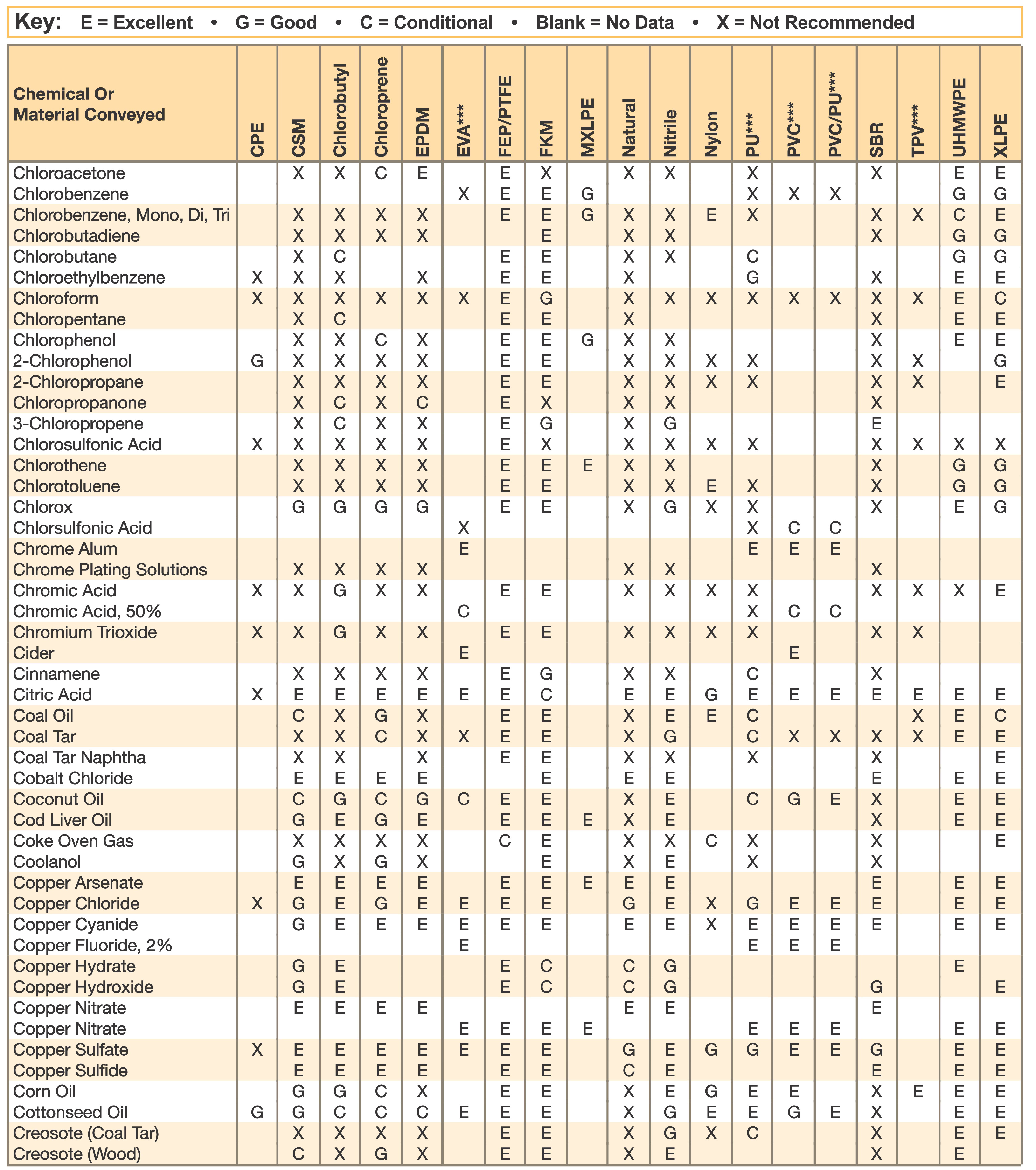
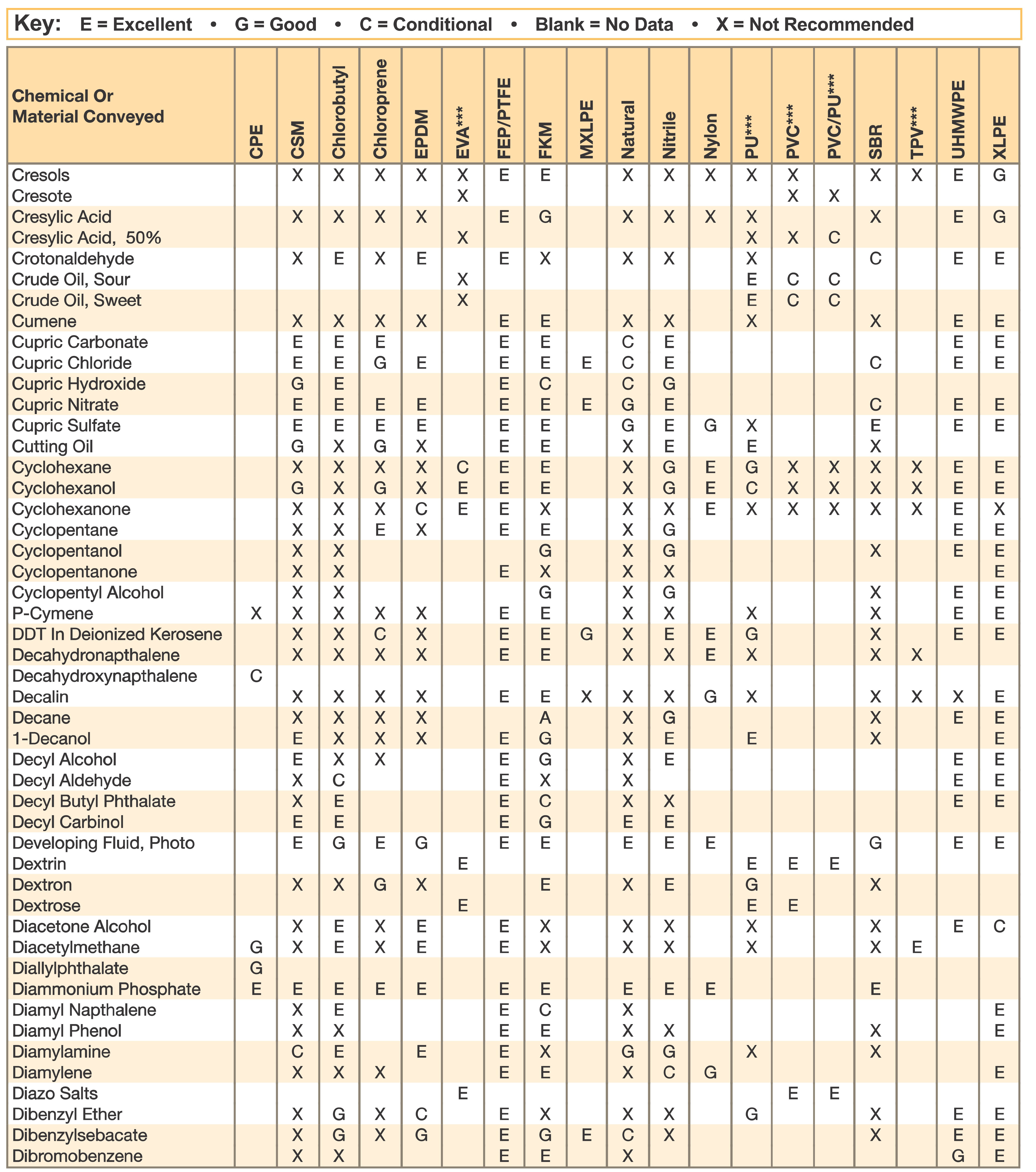
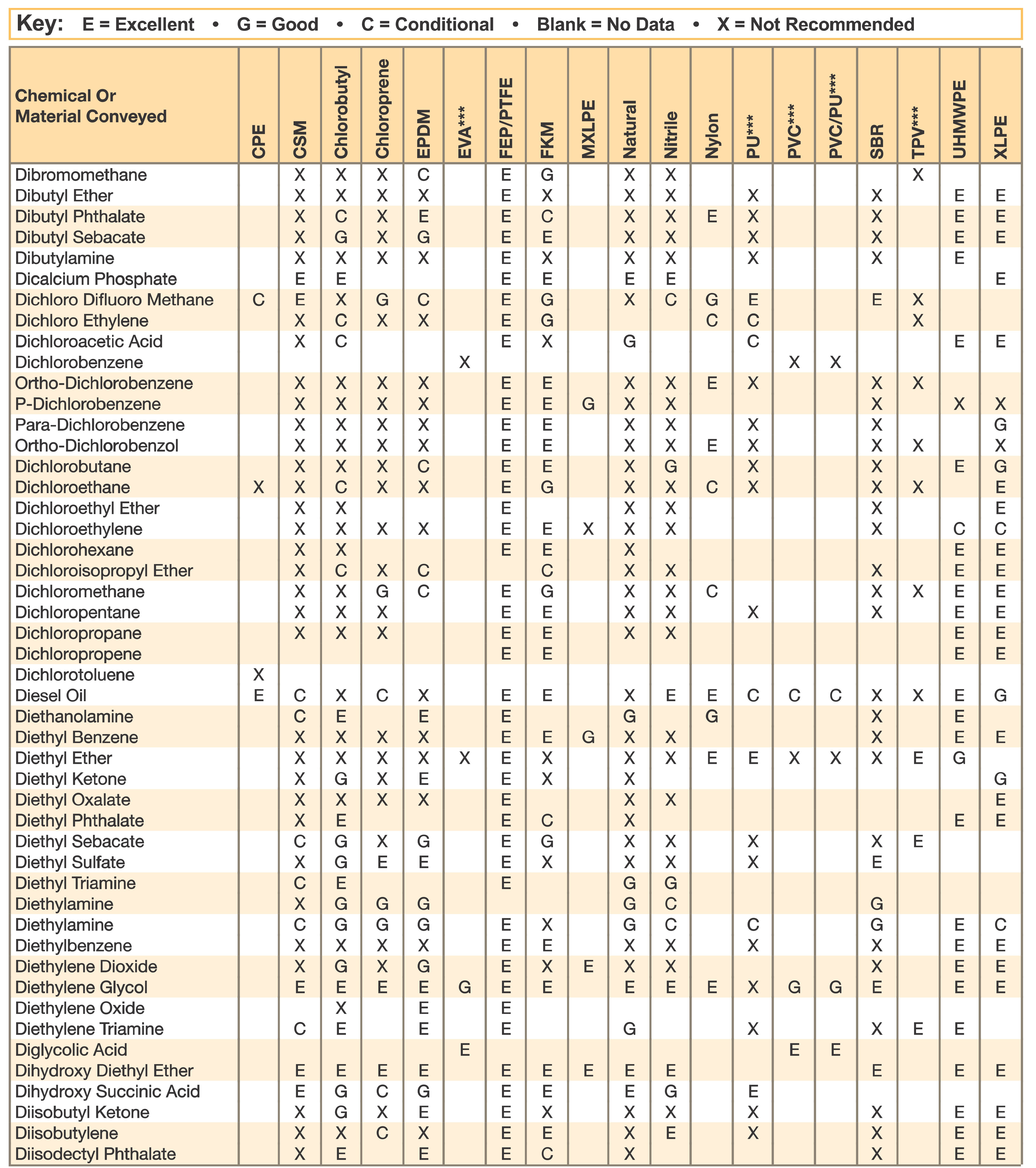
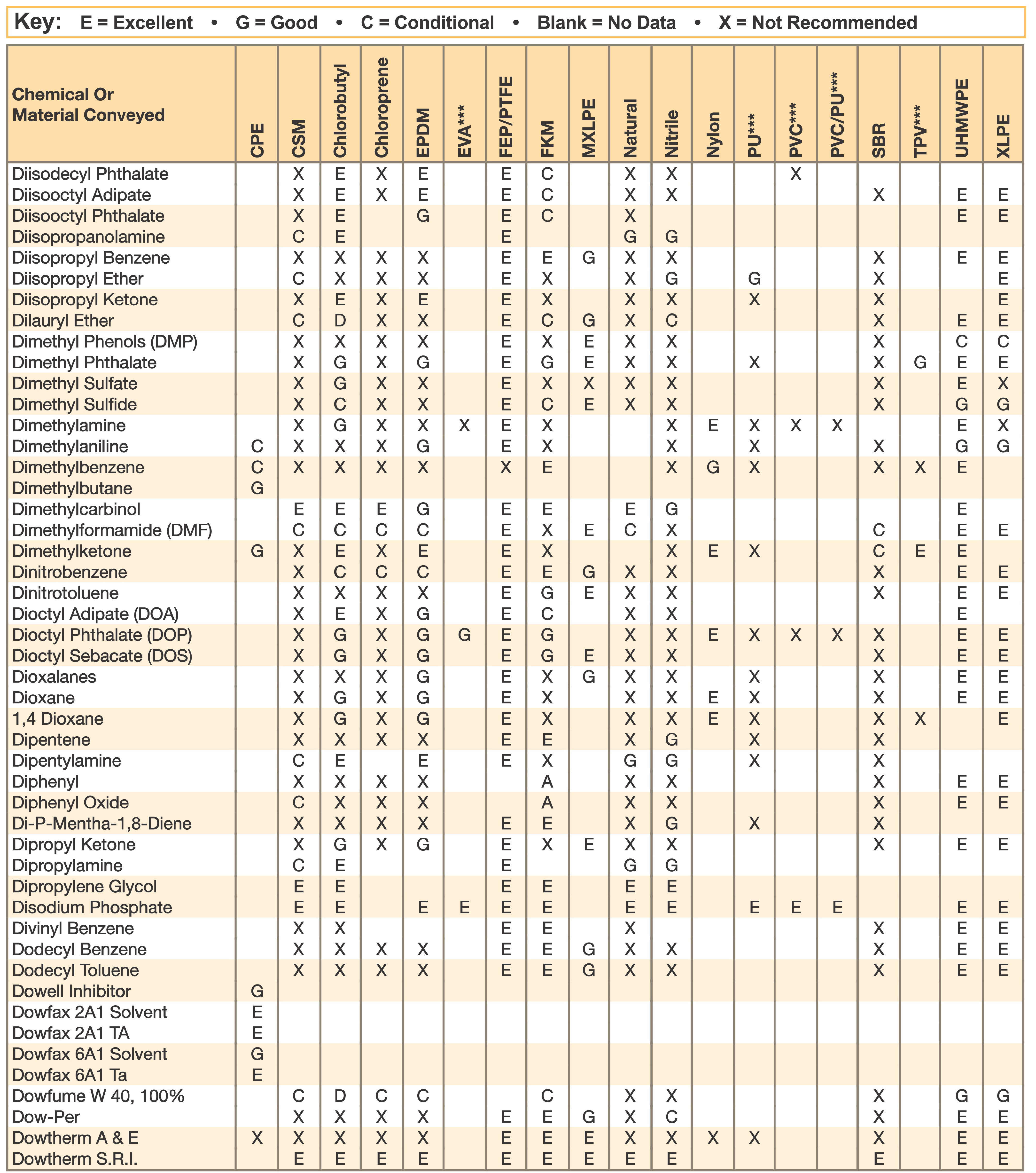
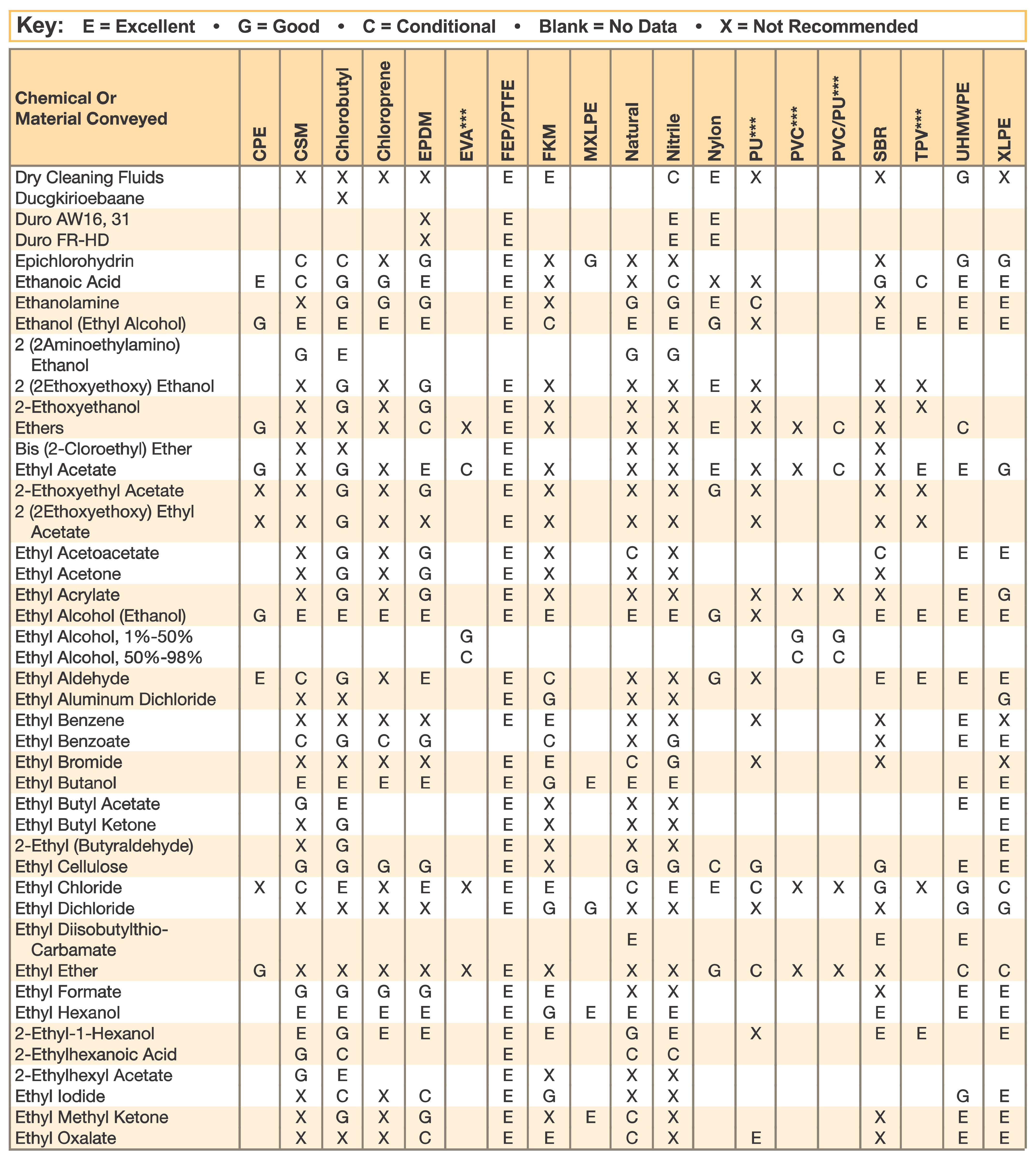
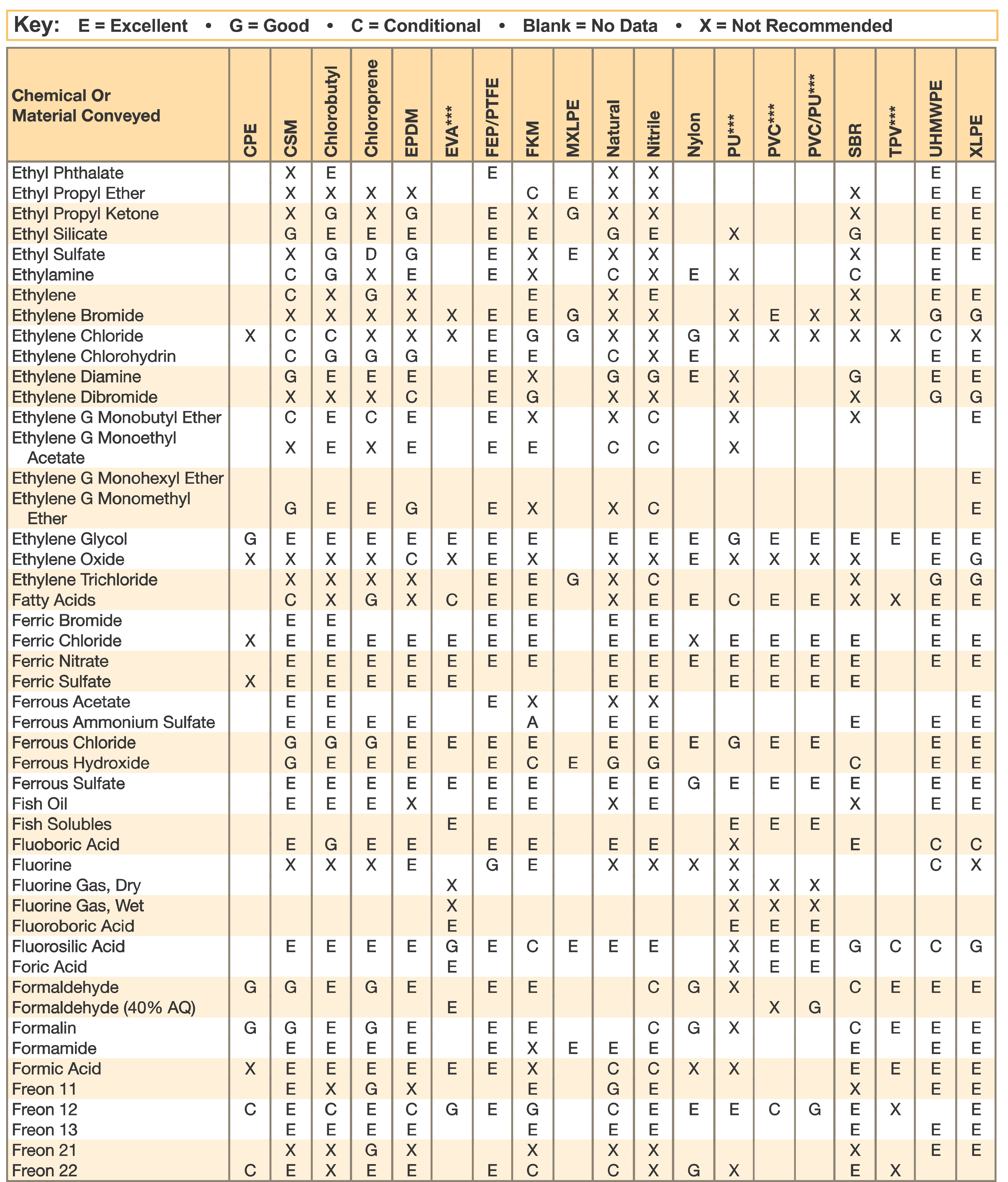
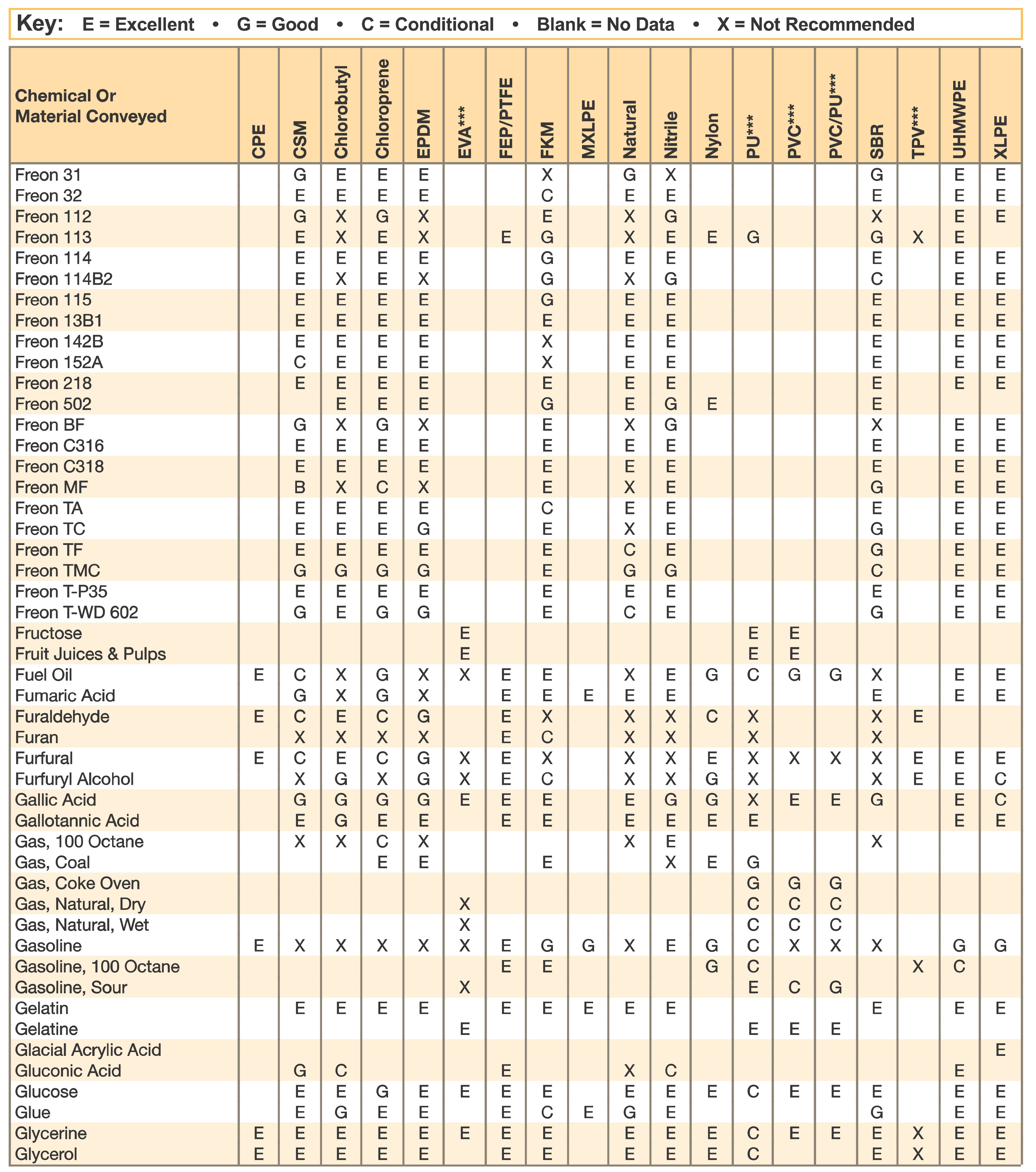
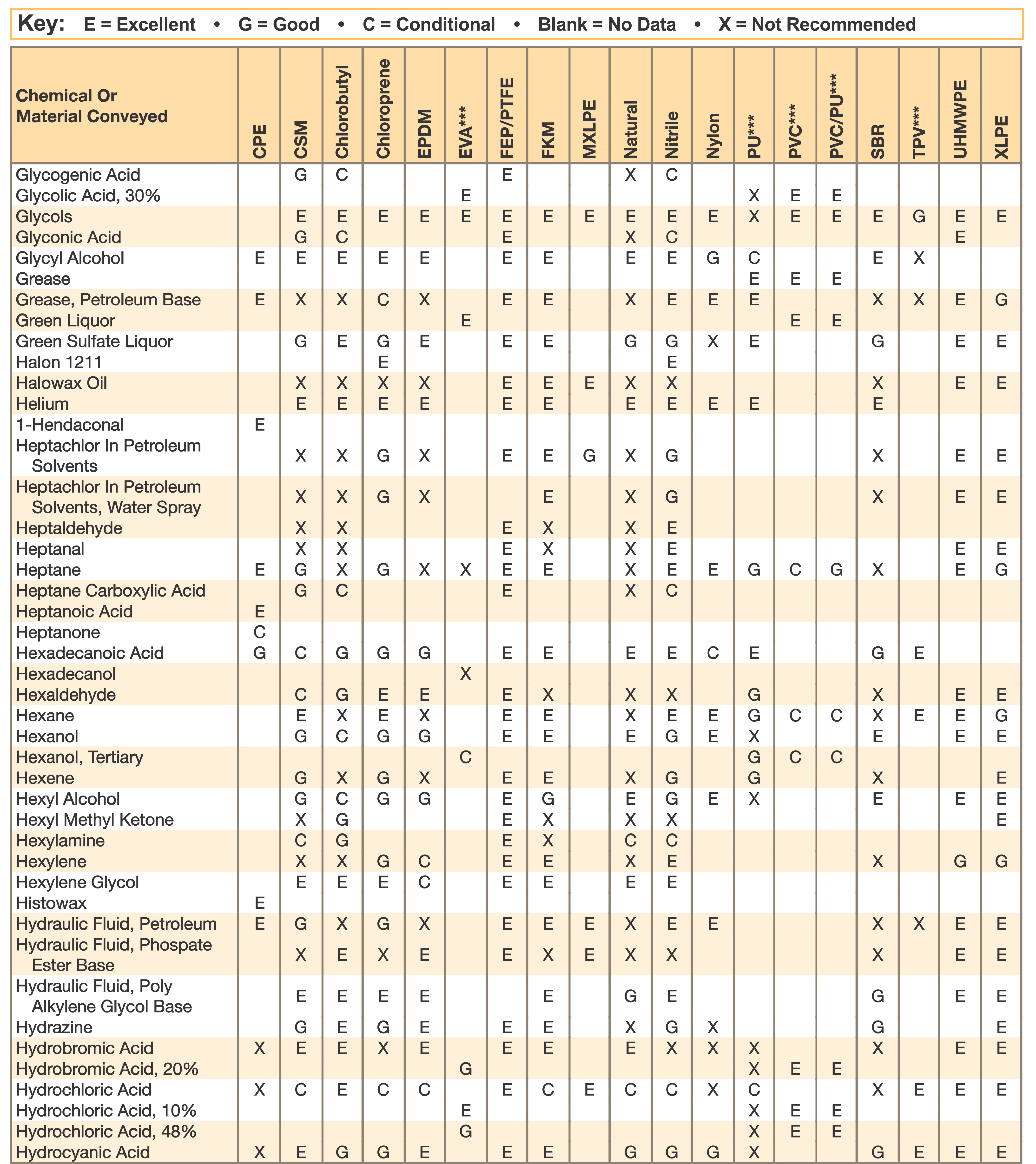
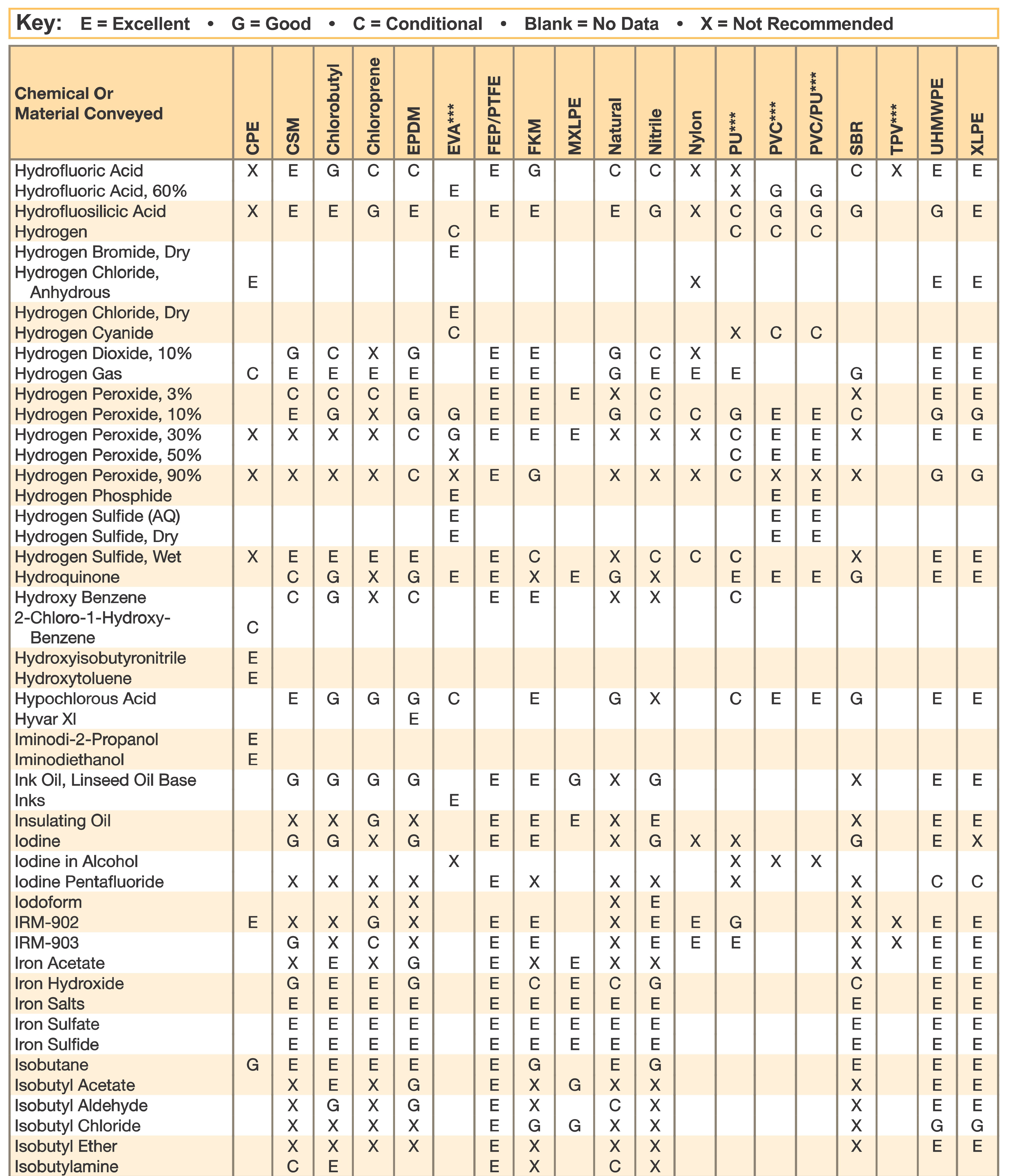
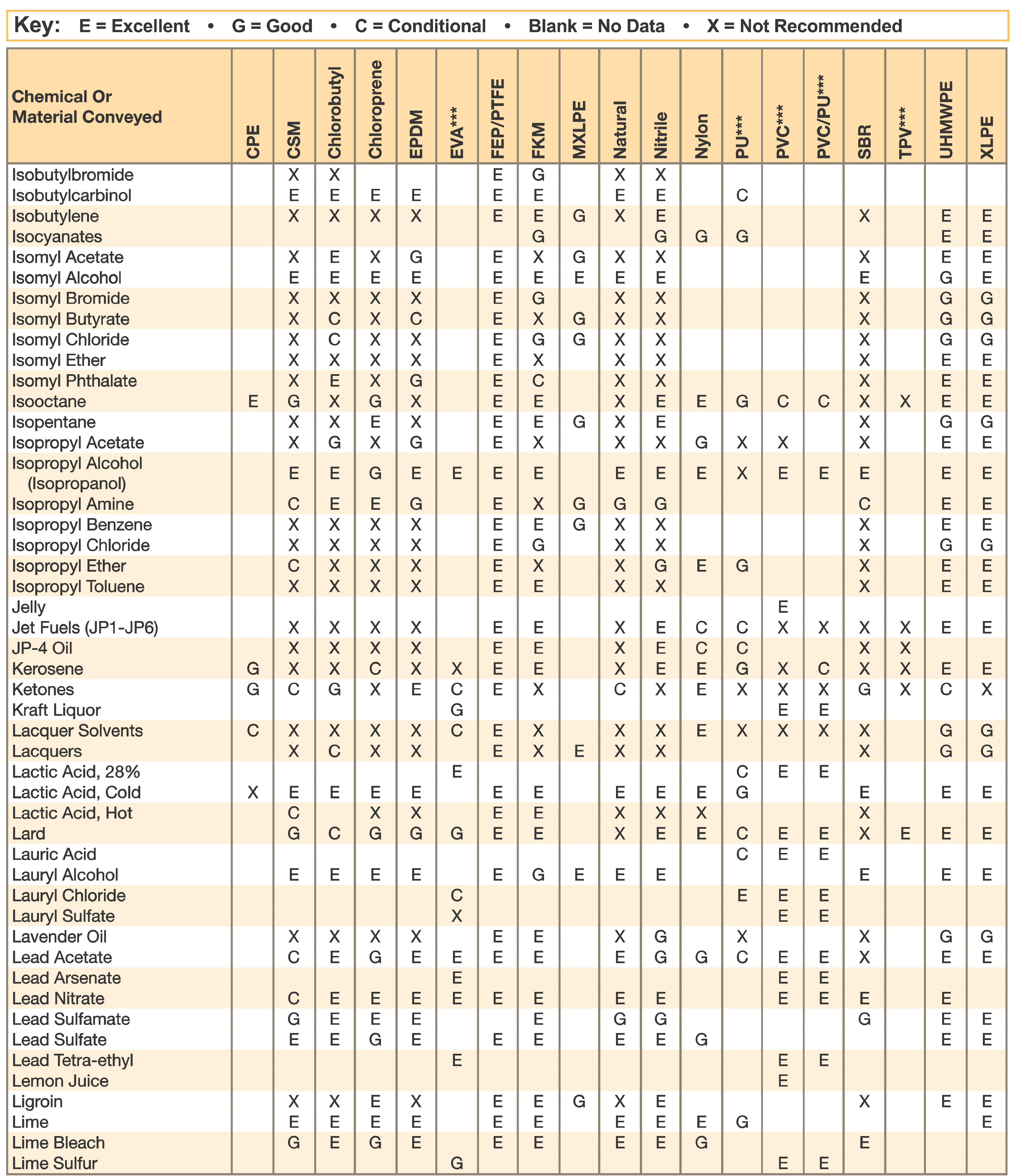
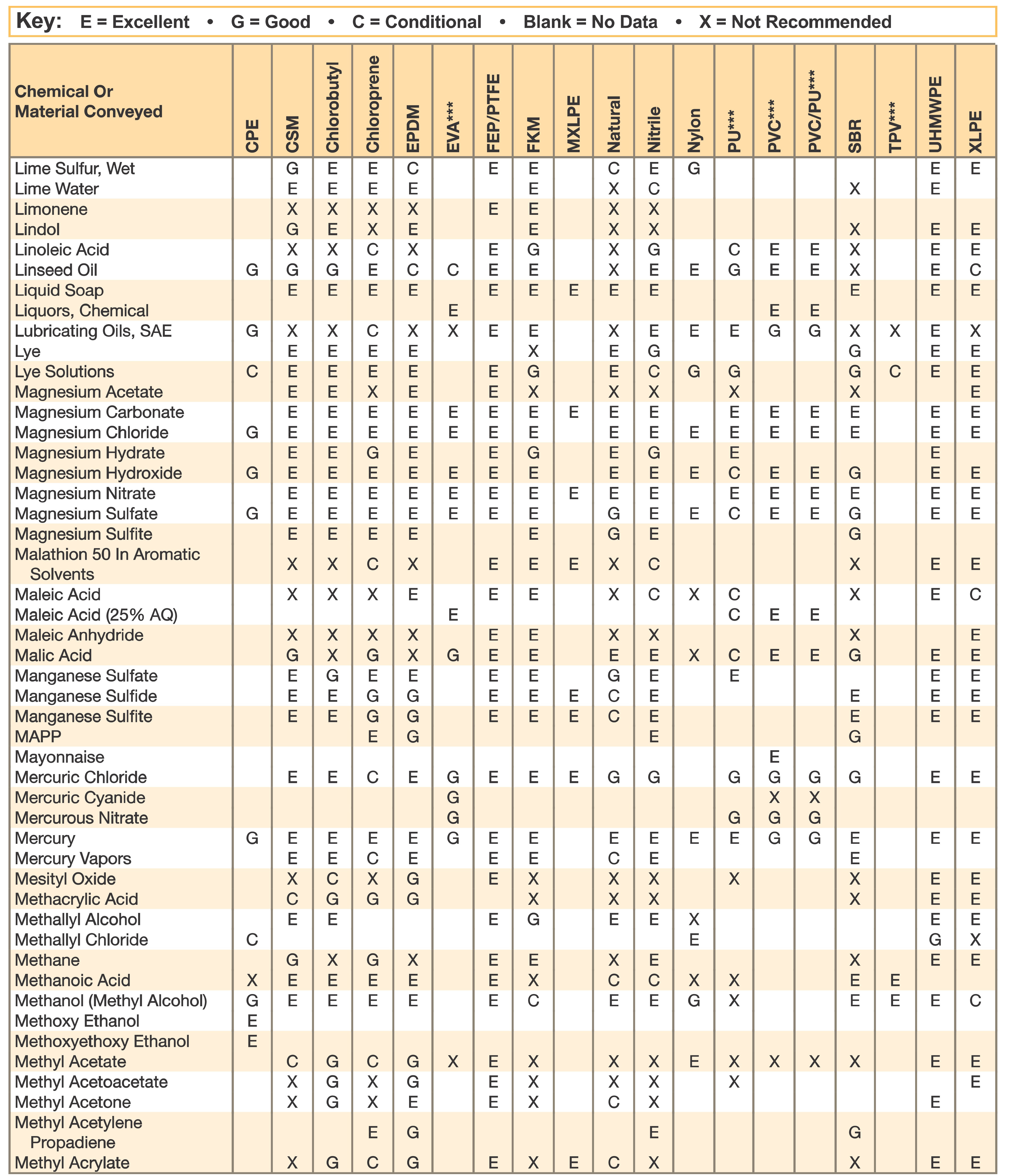
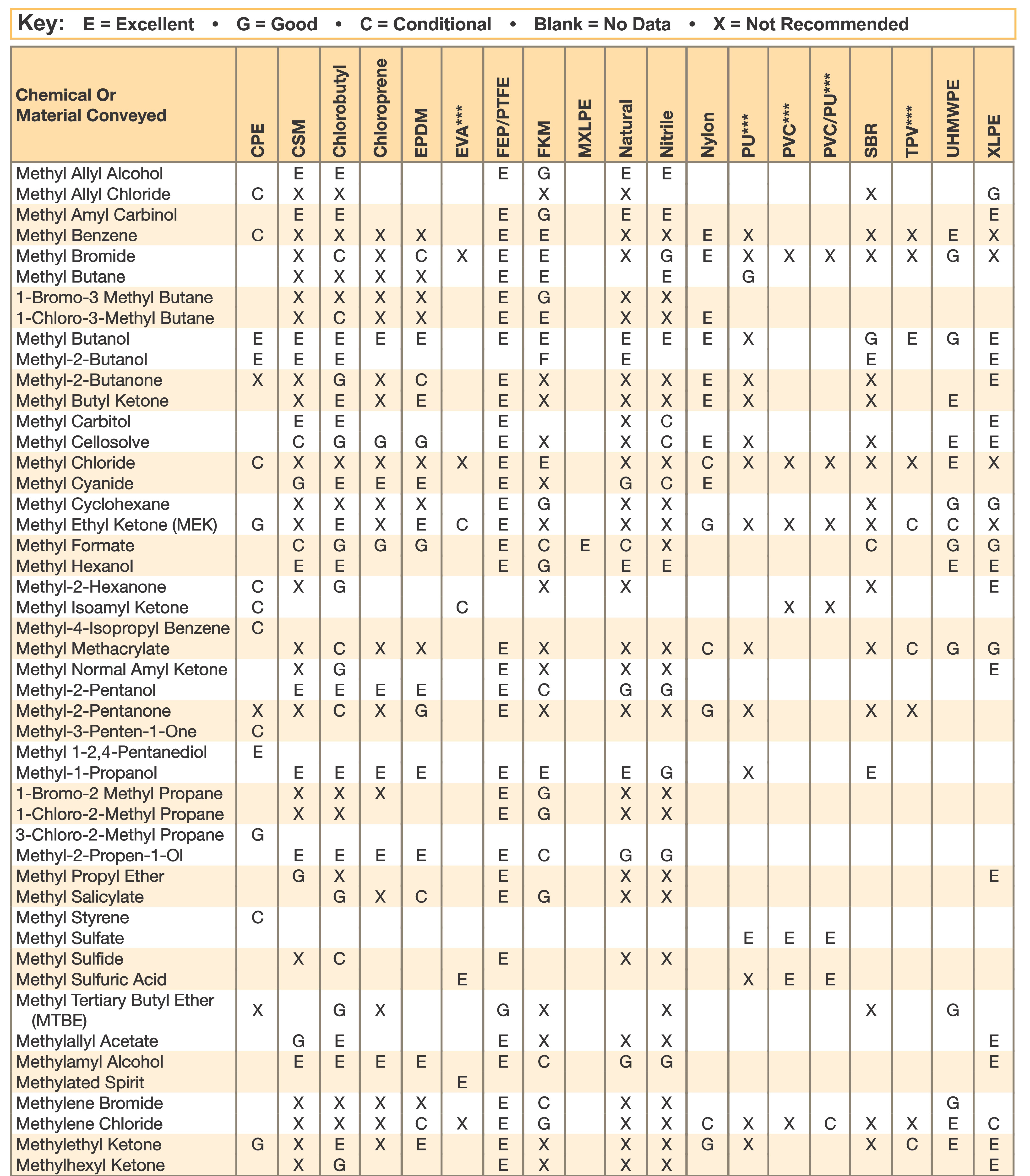
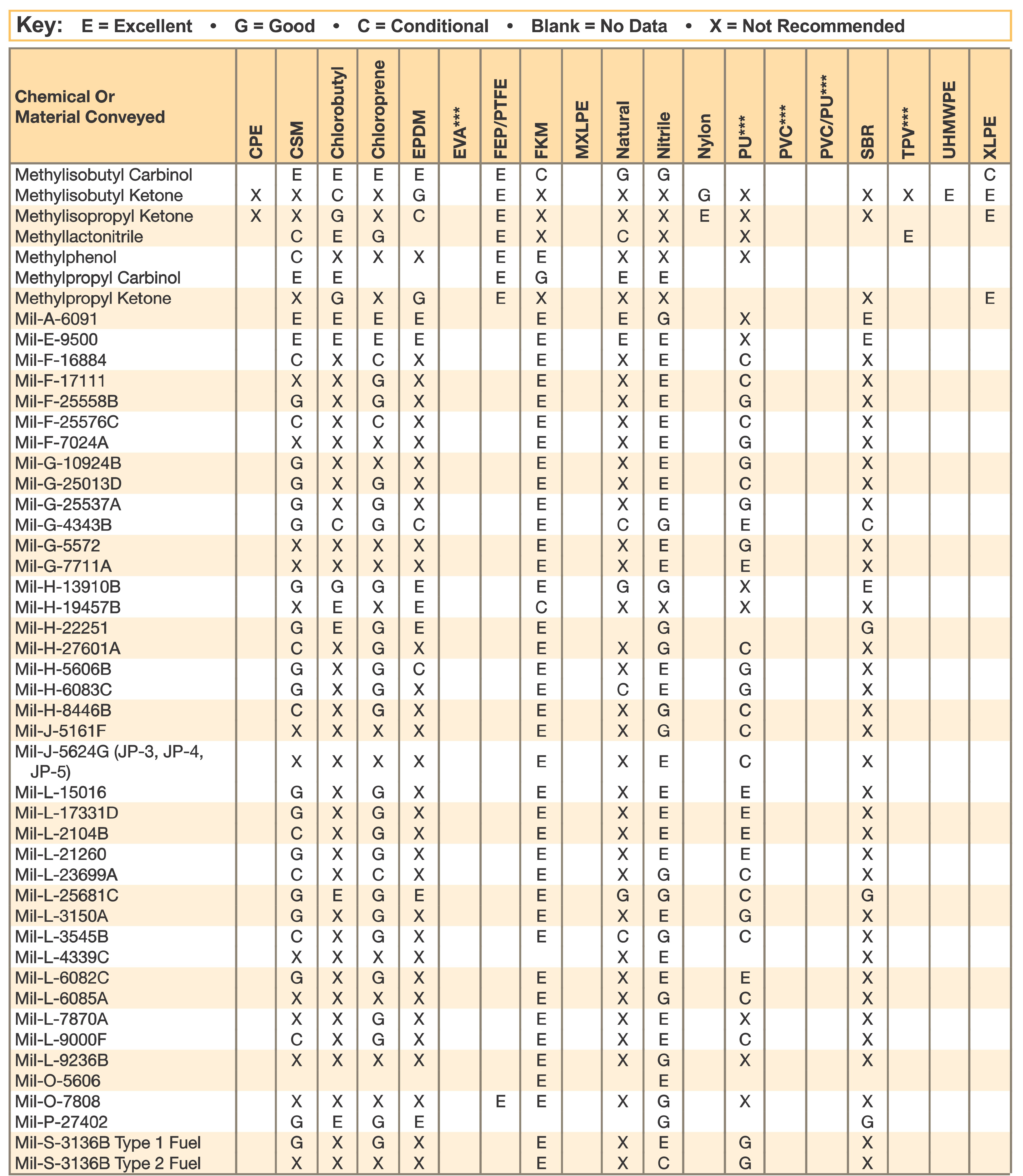
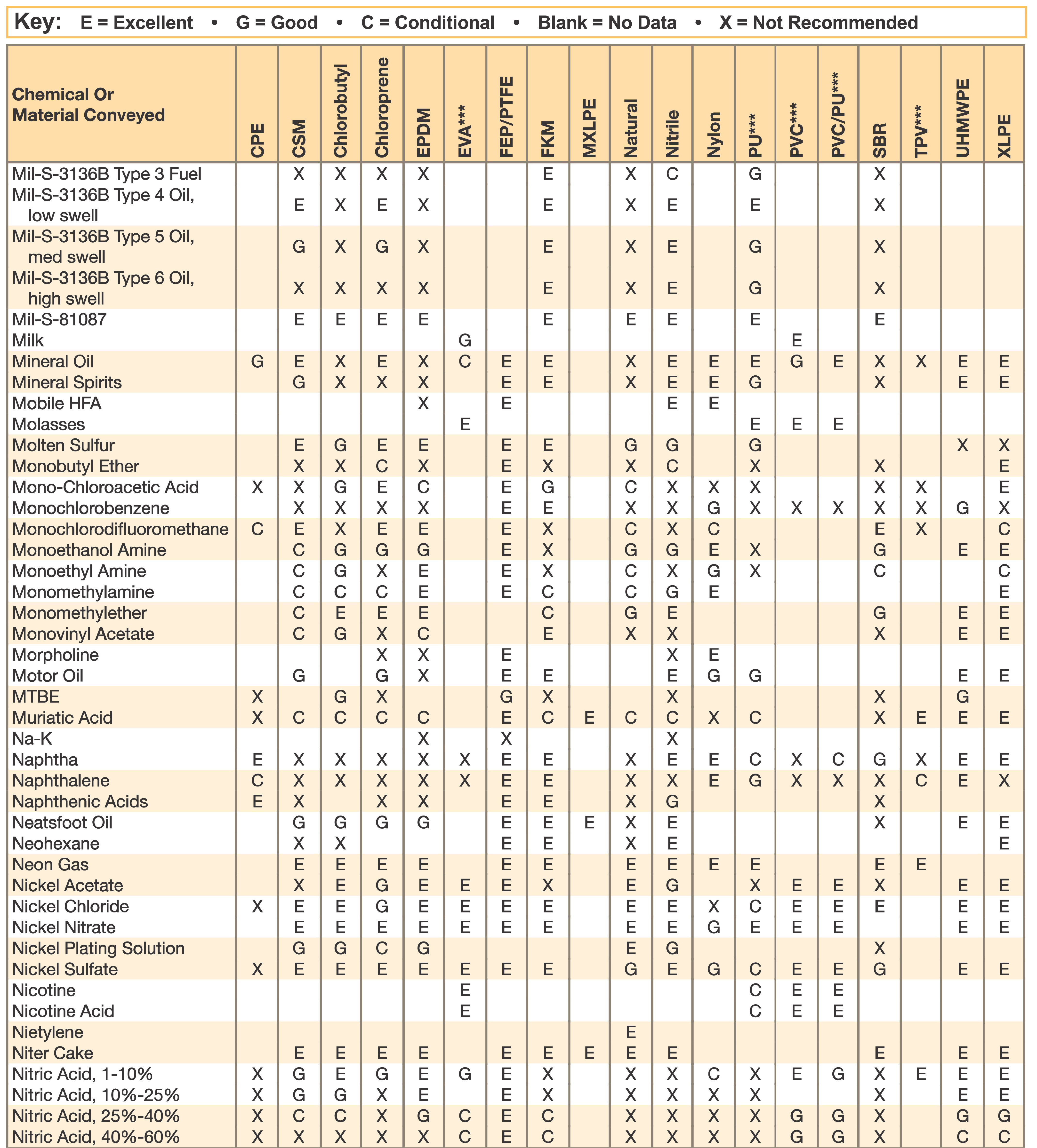
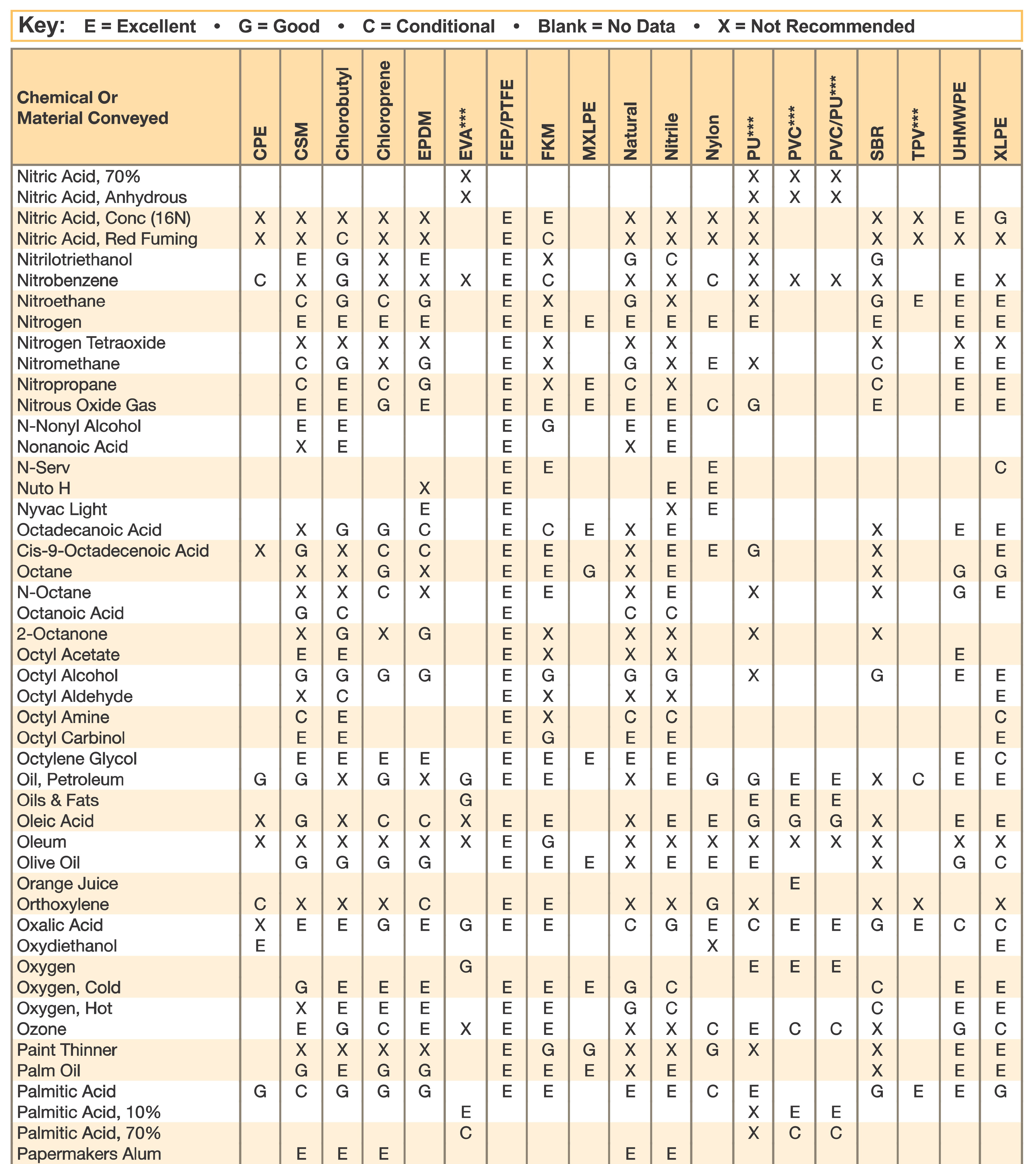
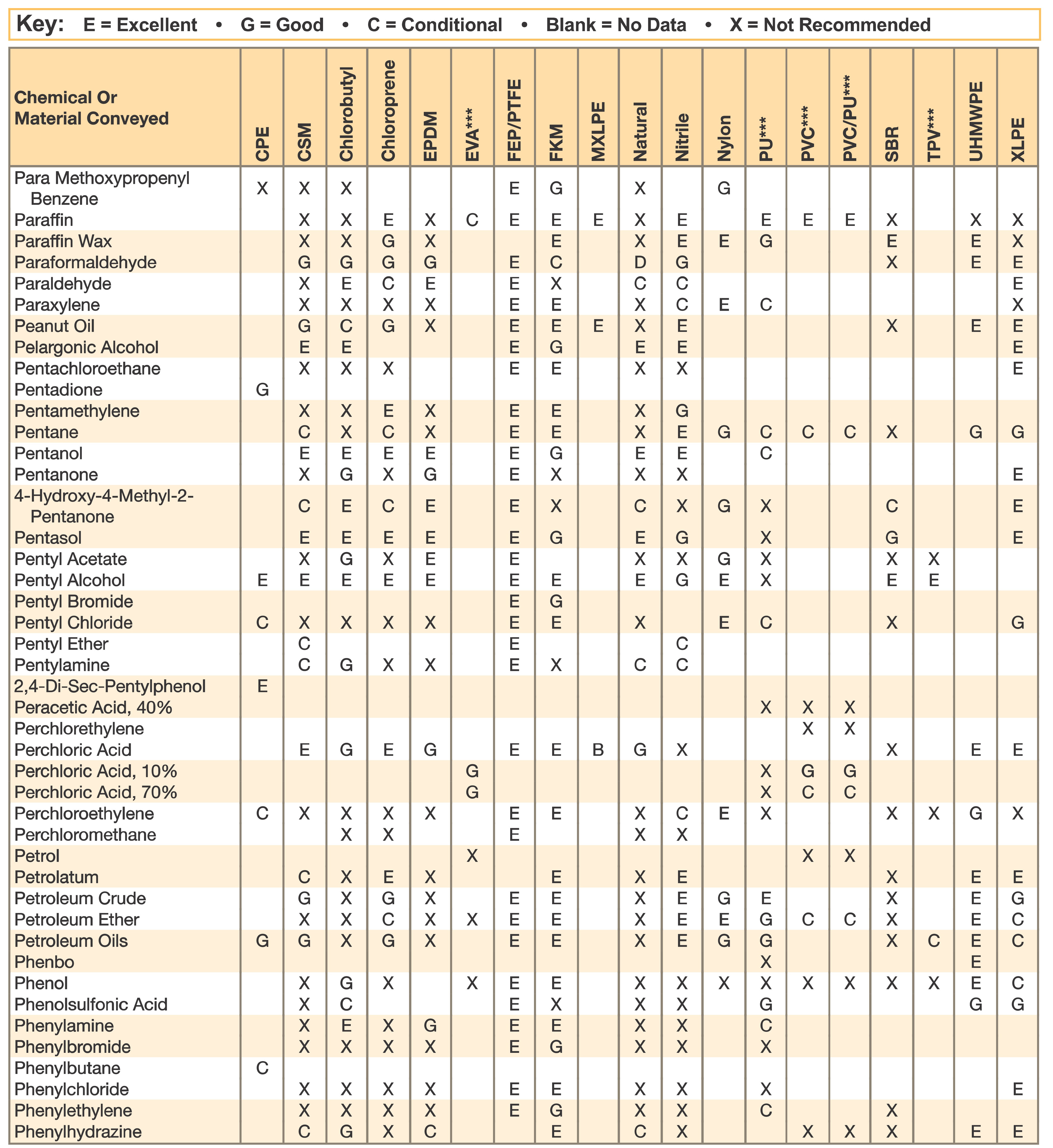
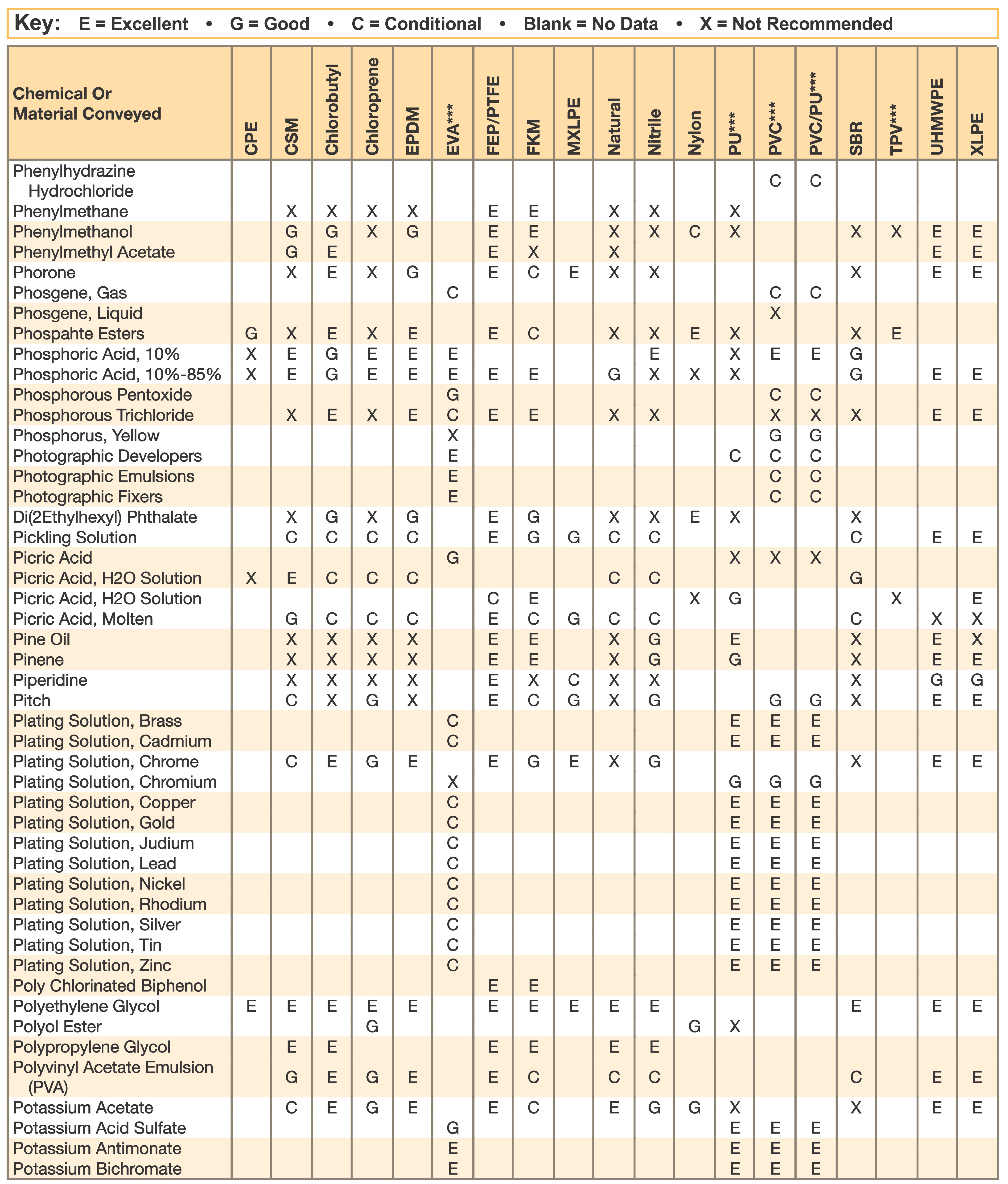
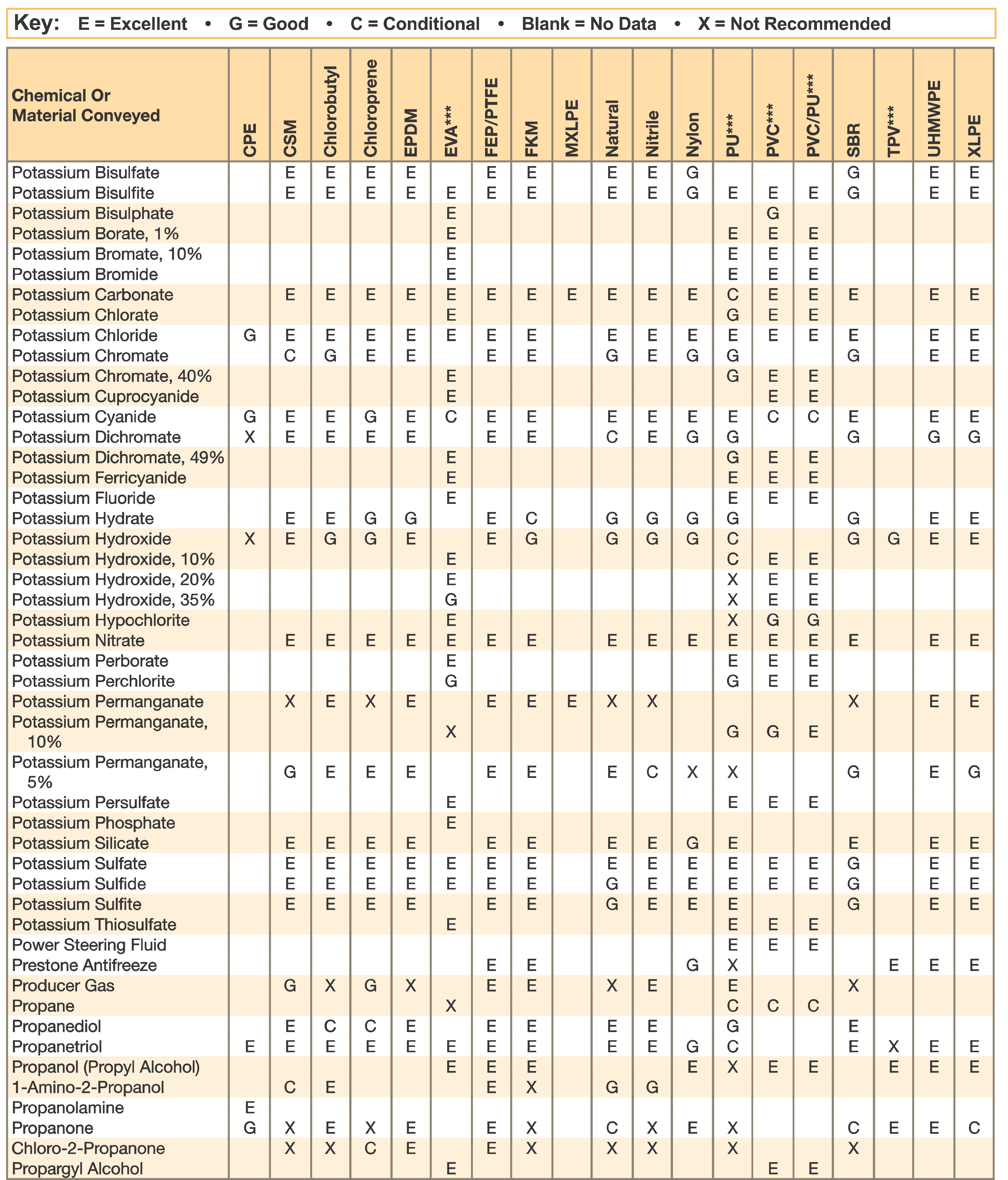
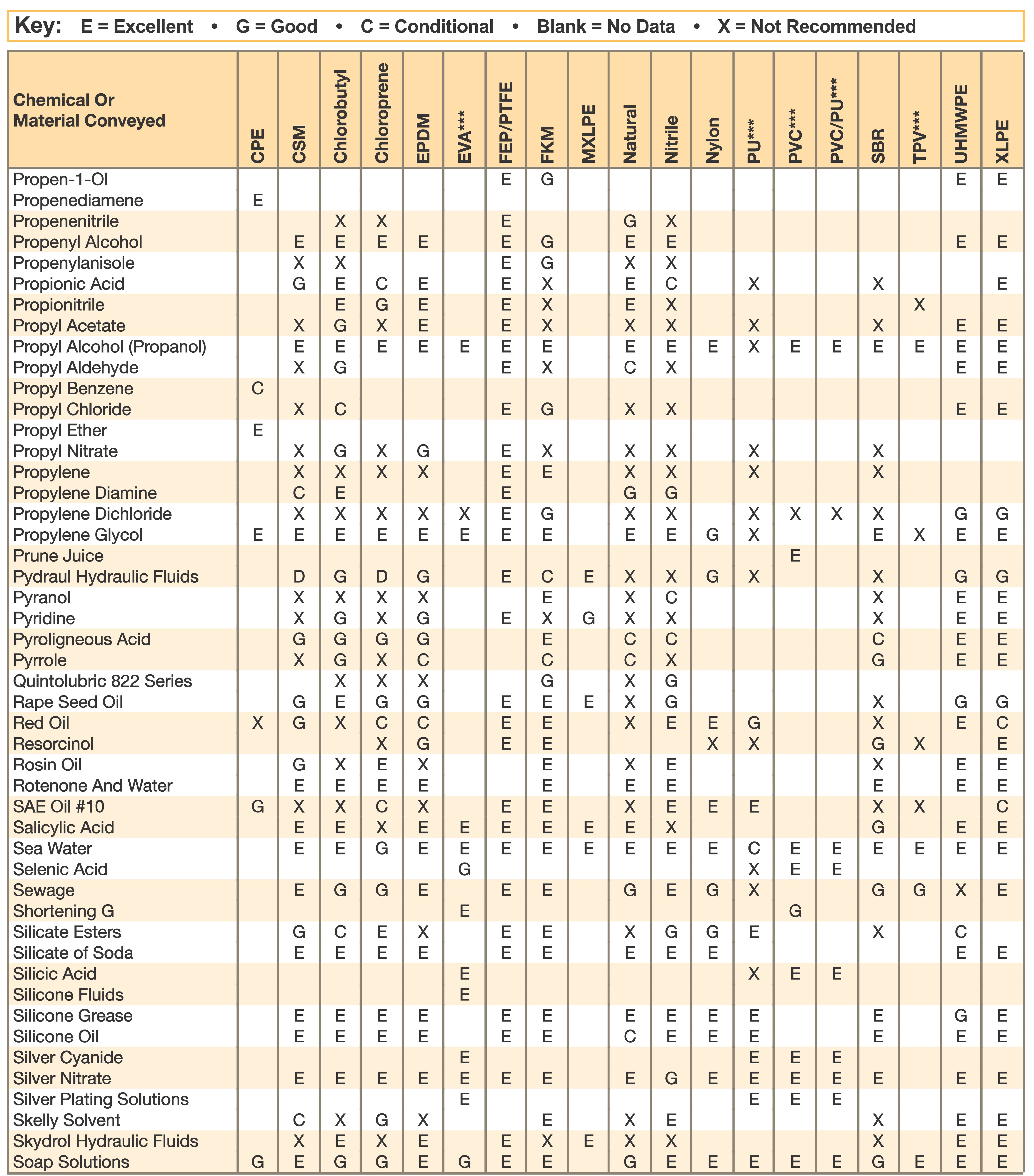
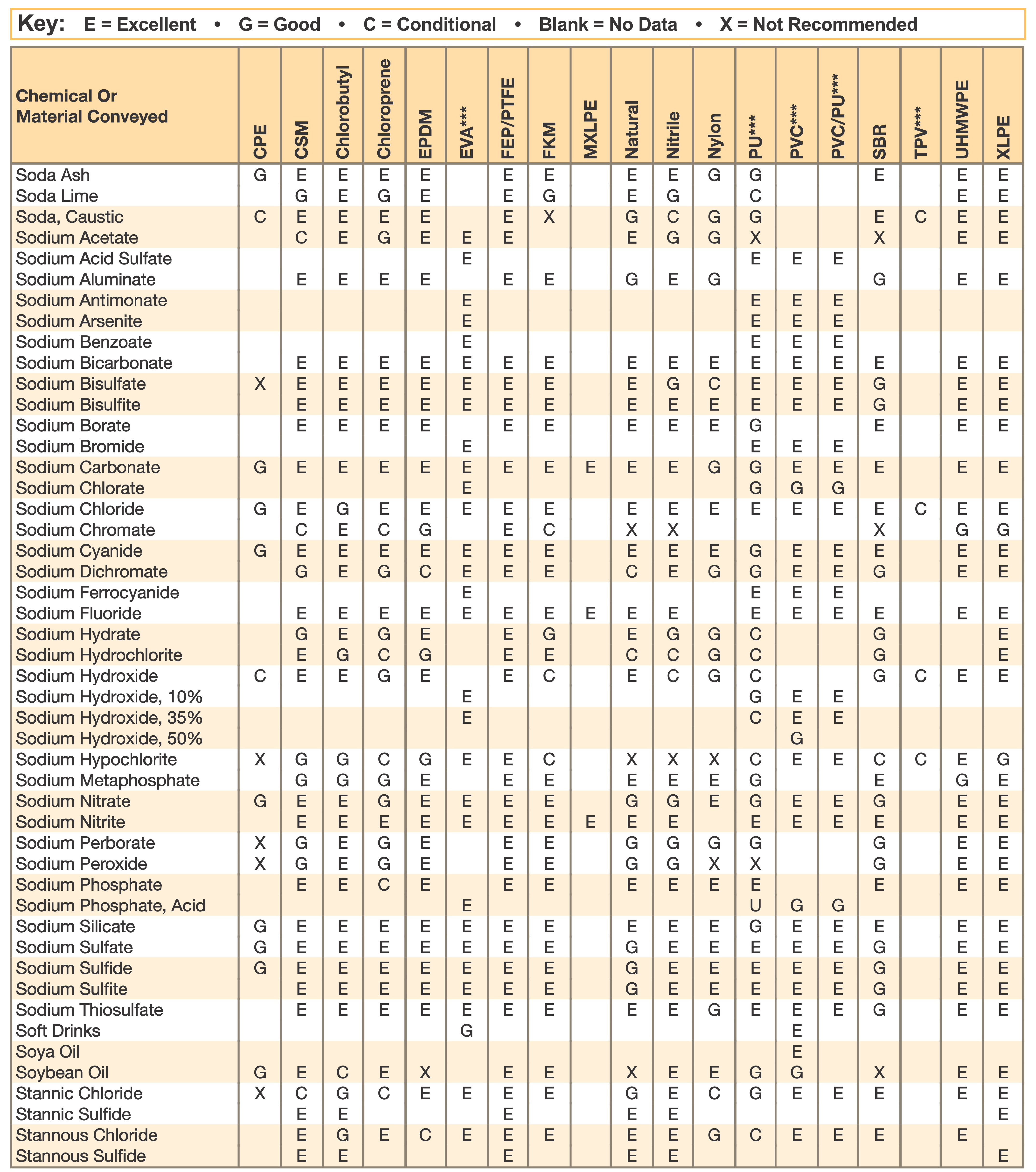
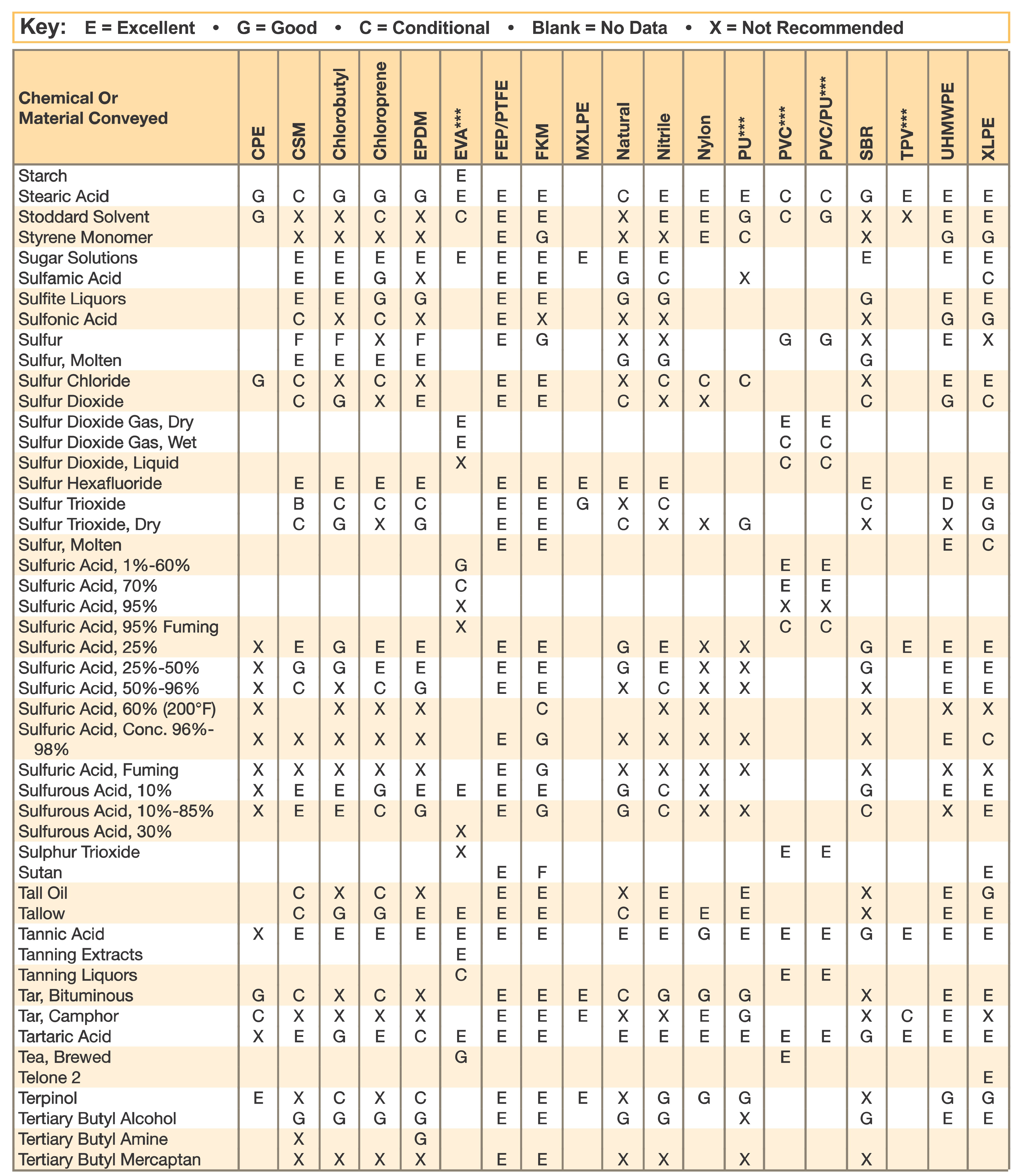
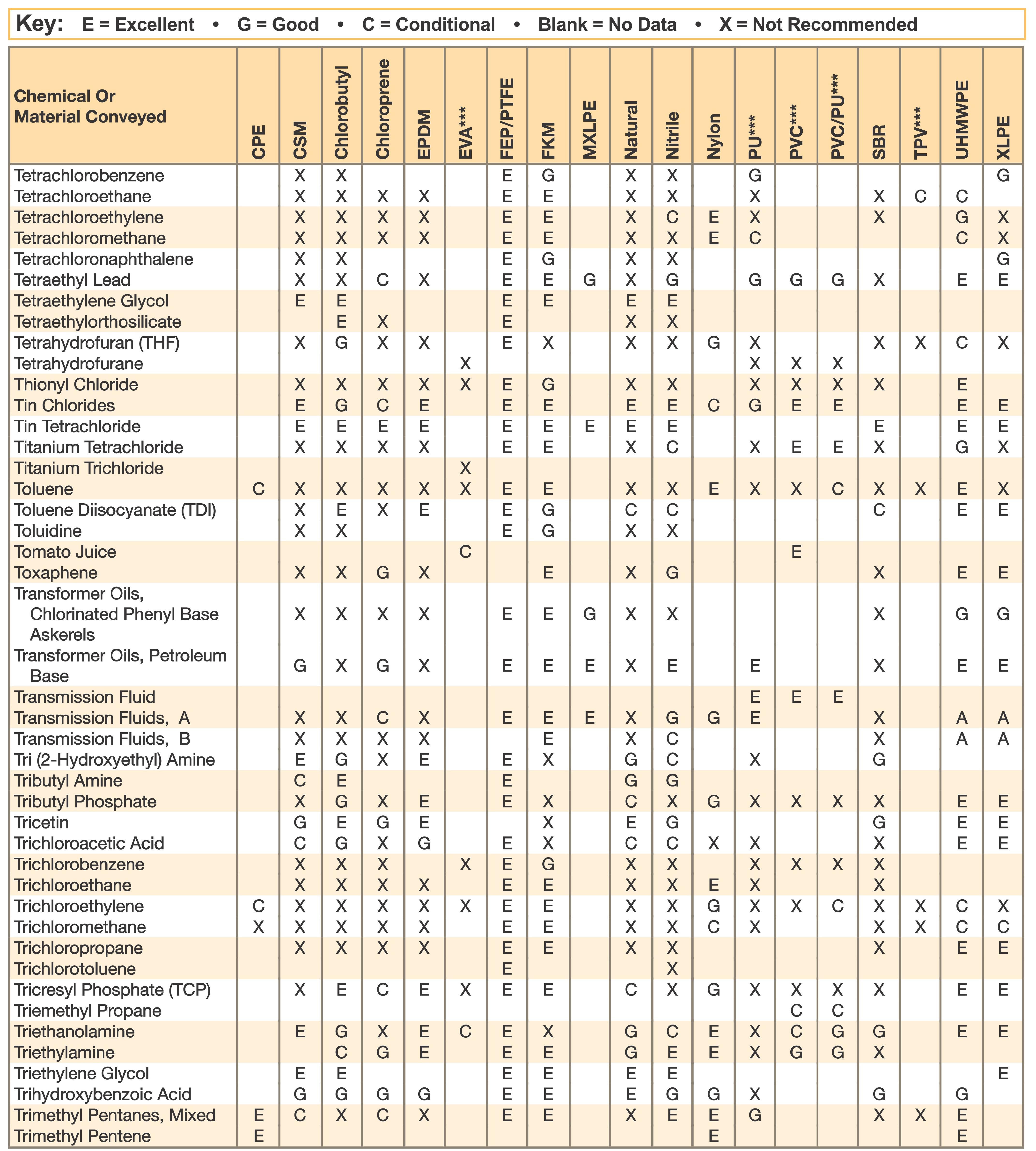
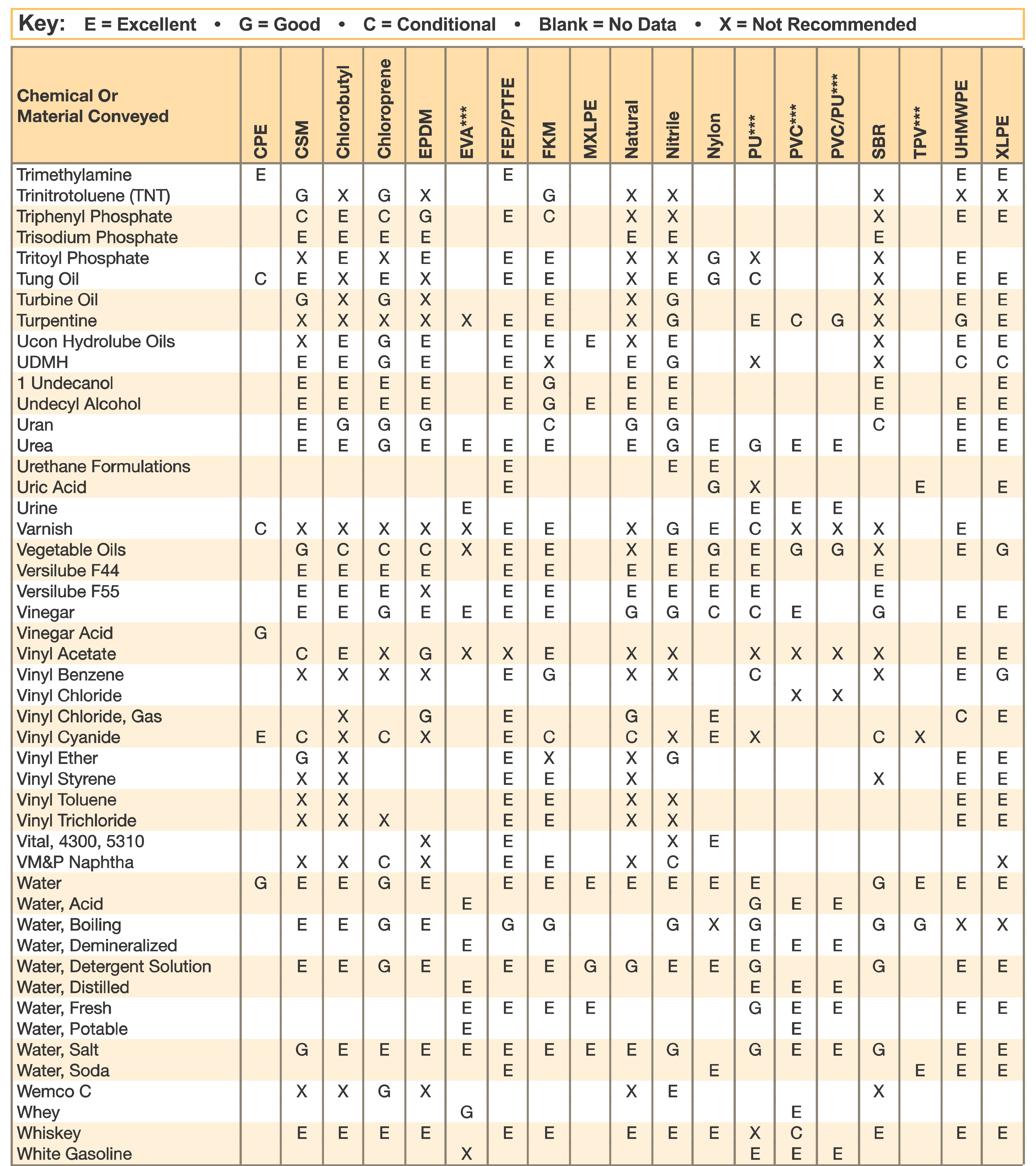
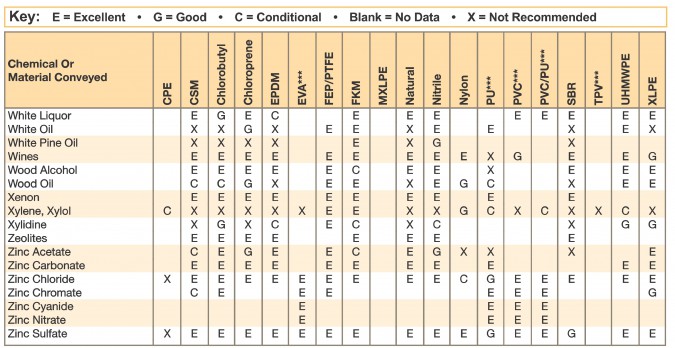
Hose and Chemical Table
The Chemical Resistance Guides in this section are offered as a general indication of the compatibility of the various compounds incorporated in Parker hose with the chemicals, fluids and media listed. This is information is available to the public provided by Parker Industrial Hose in Catalog 4800 and re-presented here by HoseandFittings.com. The basis for the ratings include actual service experience, the advice of various polymer suppliers, and the considered opinion of Parker’s chemists. When in doubt, a sample of the compound should always be tested with a particular chemical it is to handle.
Some of the variables that affect the resistance of a compound to a chemical attack are:
- Temperature of the Media Transmitted: Higher temperatures increase the affect of chemicals on compounds. The amount of increase depends upon the polymer and the chemical. A Compound quite suitable at room temperature might fail very quickly at higher temperatures. Do not operate outside the hose temperature limits. Even within hose temperature limits, end fittings and hose size can affect performance at higher temperatures.
- Service Conditions: A rubber compound usually swells when exposed to a chemical. Within a given percent of swell, a hose tube may function satisfactorily if the hose is in a static condition, but may fail quickly if the hose is subject to flexing.
- The Grade or Blend of the Rubber Compound: Basic polymers are sometimes mixed or blended to enhance a particular property fo a specific service. As an example, the nitrile used as the tube material for Parker aircraft fueling hose varies in its makeup from the nitrile used in the tube of Day-Flo® Special Purpose hose. Consequently, the reaction to a particular chemical may therefore be somewhat different. When in doubt, a sample of the compound should always be tested with a particular chemical it is going to handle.
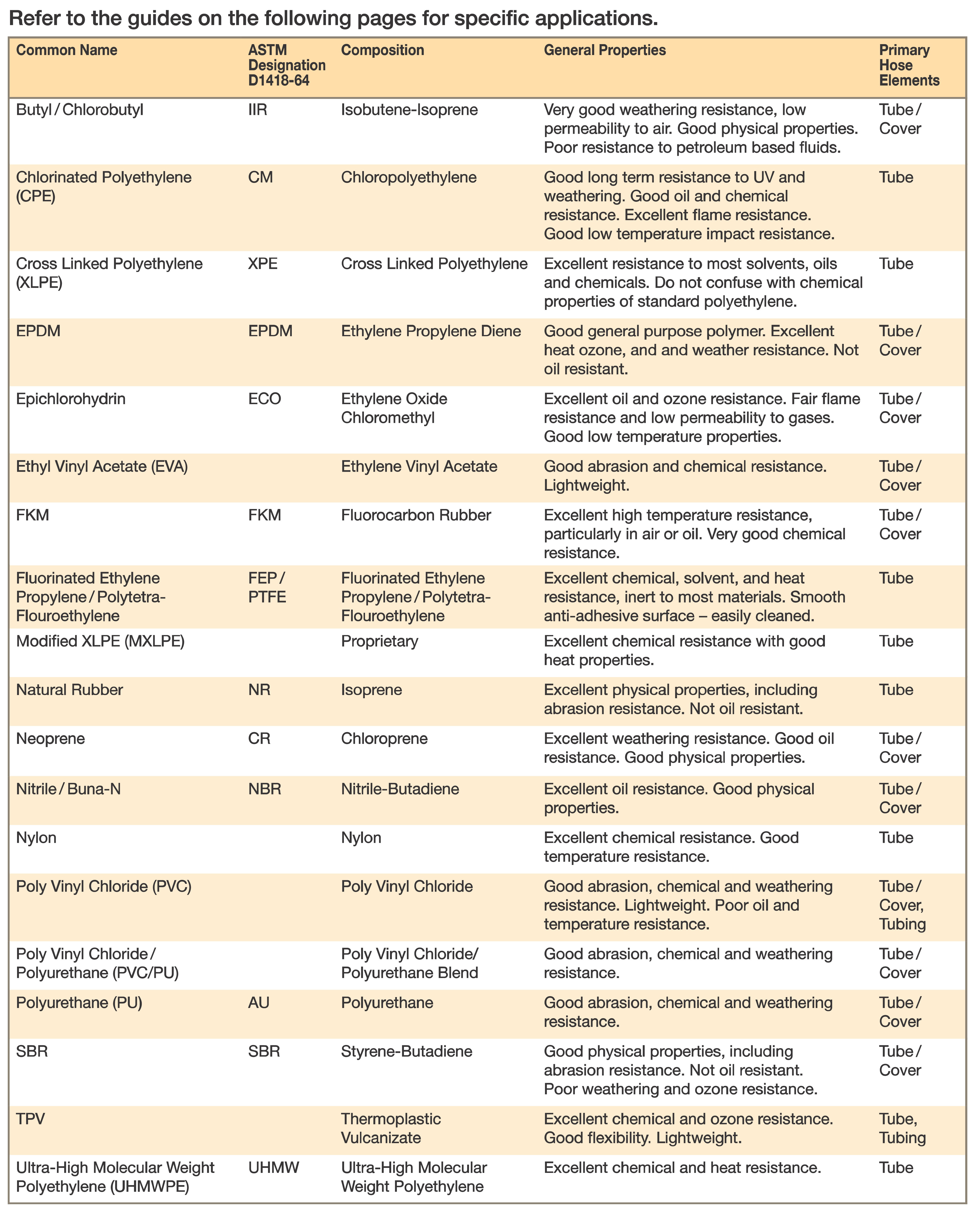
Names and General Properties of Hose Materials
Warning! The following data is based on tests and believed to be reliable; however, the tabulation should be used as a guide ONLY, since it does not take into consideration all variables, such as elevated temperatures, fluid contamination, concentration, etc., that may be encountered in actual use. All applications should be considered critical and tested in advance of their use.
*** Thermoplastic hose and tubing achieve their optimum physical properties at room temperature, 68º F. As thermoplastic materials are exposed to increased ambient temperatures, they soften and their physical properties change. For hose and tubing, heat sharply reduces the available working pressure and coupling retention. The charts below illustrate this effect. In all cases, test the product in a controlled, secure and safe environment and consider all operating prior to use.
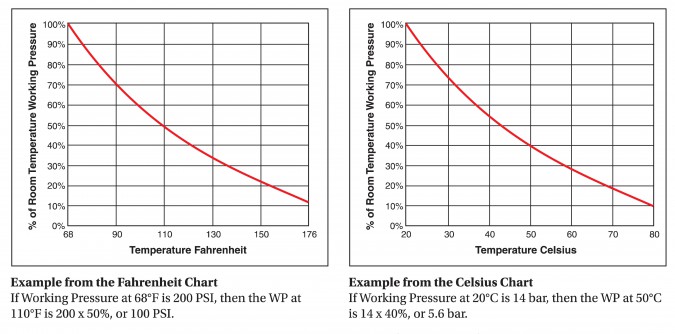
Notes:
- Data for PVC/Thermoplastic materials based on 68ºF unless otherwised noted.
- Data for other materials based on 70ºF unless otherwise noted.

Common Name / ASTM Designation D1418-64 / Composition / General Properties
- Butyl / Chlorobutyl / IIR / Isobutene-Isoprene / Very good weathering resistance, low permeability to air. Good physical properties. Poor resistance to petroleum based fluids.
- Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) / CM / Chloropolyethylene / Good long term resistance to UV and weathering. Good Oil and chemical resistance. Excellent flame resistance. Good low temperature impact resistance.
- Cross Linked Polyethylene (XLPE) / XPE / Cross Linked Polyethylene / Excellent resistance to most solvents, oils and chemicals. Do not confuse with chemical properties of standard polyethylene.
- EPDM / EPDM / Ethylene Propylene Diene / Good General Purpose Polymer. Excellent heat ozone, and weather resist.
- Epichlorohydrin / ECO / Ethylene Oxide Chloromethyl / Excellent oil resistance. Fair flame resistance and low permeability to gases. Good low temperature properties.
- Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA) / / Ethylene Vinyl Acetate / Good abrasion and chemical resistance. Lightweight.
- FKM / FKM / Florocarbon Rubber / Excellent high temperature resistance, particularly in air or oil. Very good chemical resistance.
- Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene / Polytetra-Flouroethylene / FEP / PTFE / Excellent chemical solvent, and heat resistance, inert to most materials. Smooth anti-adhesive surface – easily cleaned.
- Natural Rubber / NR / Isoprene / Excellent physical properties, including abrasion resistance. Not oil resistant.
- Neoprene / CR / Chloroprene / Excellent weathering resistance. Good oil resistance. Good physical properties.
- Nitrile / Buna-N / NBR / Nitrile-Butadiene / Excellent oil resistance. Good physical properties.
- Nylon / / Nylon / Excellent chemical resistance. Good temperature resistance.
- Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC) / / Poly Vinyl Chloride / Good abrasion, chemical and weathering resistance. Lightweight. Poor oil and temperature resistance.
- Poly Vinyl Chloride / Polyurethane (PCV/PU) / / Poly Vinyl Chloride/Polyurethane Blend / Good abrasion, chemical and weathering resistance.
- Polyurethane (PU) / AU / Polyurethane / Good abrasion, chemical and weathering resistance
- SBR / SBR / Styrene-Butadiene / Good physical properties, including abrasion resistance. Not oil resistant. Poor weathering and ozone resistance.
- TPV / / Thermoplastic Vulcanizate / Excellent chemical and ozone resistance. Good flexibility. Lightweight.
- Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethanylene (UHMWPE) / UHMW / Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene / Excellent chemical and heat resistance.
Source of Information: Parker Industrial Hose Catalog 4800 October 2011 Full Line

